 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Cine Sequence' found in 1 term [ ] and 1 definition [ ] and 1 definition [ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 21) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Cine Sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
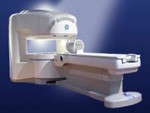
From GE Healthcare;
the Signa Ovationâ„¢ is a patient-friendly open MRI scanner designed not only to handle a typical patient mix, but to accommodate larger patients, patients who are claustrophobic, and others who have difficulty tolerating the close quarters of conventional MR machines.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Standard: SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE and SPGR, 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D FSE, 2D/3D FGRE and FSPGR, SSFP, FLAIR, EPI, optional: 2D/3D Fiesta, true chem sat, fat/water separation, single shot diffusion EPI, line scan diffusionIMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF TR 1.3 to 12000 msec in increments of 1 msec TE 0.4 to 2000 msec in increments of 1 msec 2D: 1.4mm - 20mm 3D: 0.2mm - 20mm 0.08 mm; 0.02 mm optional POWER REQUIREMENTS 200 - 480, 3-phase MAX. GRADIENT AMPLITUDE 19 mT/m | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
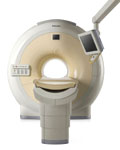
From Philips Medical Systems;
The clinical capabilities of MR will further expand. Inside and out, the Achieva is a friendly, open system designed for optimal patient comfort and maximized workflow with high functionality.
The Achieva 1.5T can be upgraded to Achieva I/T, with three configurations optimized for MR guided interventions and therapy:
•
Achieva I/T Neurosurgery
•
Achieva I/T Cardiovascular (or XMR - combining an Achieva 1.5T CV system and an X-Ray system)
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
Standard: Head, body, C1, C3; Optional: Small joint, flex-E, flex-R, endocavitary (L and S), dual TMJ, knee, neck, T/L spine, breast; optional phased array: Spine, pediatric, 3rd party connector; Optional SENSEâ„¢ coils for all applications
SE, Modified-SE, IR (T1, T2, PD), STIR, FLAIR, SPIR, FFE, T1-FFE, T2-FFE, Balanced FFE, TFE, Balanced TFE, Dynamic, Keyhole, 3D, Multi Chunk 3D, Multi Stack 3D, K Space Shutter, MTC, TSE, Dual IR, DRIVE, EPI, Cine, 2DMSS, DAVE, Mixed Mode; Angiography: Inflow MRA, TONE, PCA, CE MRA
128 x 128, 256 x 256,512 x 512,1024 x 1024 (64 for Bold img)
Variable in 1% increments
Lum.: 120 cd/m2; contrast: 150:1
Variable (op. param. depend.)
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380/400 V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Intera Achieva 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
•
In the 1930's, Isidor Isaac Rabi (Columbia University) succeeded in detecting and measuring single states of rotation of atoms and molecules, and in determining the mechanical and magnetic moments of the nuclei.
•
Felix Bloch (Stanford University) and Edward Purcell (Harvard University) developed instruments, which could measure the magnetic resonance in bulk material such as liquids and solids. (Both honored with the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1952.) [The birth of the NMR spectroscopy]
•
In the early 70's, Raymond Damadian (State University of New York) demonstrated with his NMR device, that there are different T1 relaxation times between normal and abnormal tissues of the same type, as well as between different types of normal tissues.
•
In 1973, Paul Lauterbur (State University of New York) described a new imaging technique that he termed Zeugmatography. By utilizing gradients in the magnetic field, this technique was able to produce a two-dimensional image (back-projection). (Through analysis of the characteristics of the emitted radio waves, their origin could be determined.) Peter Mansfield further developed the utilization of gradients in the magnetic field and the mathematically analysis of these signals for a more useful imaging technique. (Paul C Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield were awarded with the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medi cine.)
•
1977/78: First images could be presented.
A cross section through a finger by Peter Mansfield and Andrew A. Maudsley.
Peter Mansfield also could present the first image through the abdomen.
•
In 1977, Raymond Damadian completed (after 7 years) the first MR scanner (Indomitable). In 1978, he founded the FONAR Corporation, which manufactured the first commercial MRI scanner in 1980. Fonar went public in 1981.
•
1981: Schering submitted a patent application for Gd-DTPA dimeglumine.
•
1982: The first 'magnetization-transfer' imaging by Robert N. Muller.
•
In 1983, Toshiba obtained approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan for the first commercial MRI system.
•
1986: Jürgen Hennig, A. Nauerth, and Hartmut Friedburg (University of Freiburg) introduced RARE (rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement) imaging. Axel Haase, Jens Frahm, Dieter Matthaei, Wolfgang Haenicke, and Dietmar K. Merboldt (Max-Planck-Institute, Göttingen) developed the FLASH ( fast low angle shot) sequence.
•
1988: Schering's MAGNEVIST gets its first approval by the FDA.
•
In 1991, fMRI was developed independently by the University of Minnesota's Center for Magnetic Resonance Research (CMRR) and Massachusetts General Hospital's (MGH) MR Center.
•
From 1992 to 1997 Fonar was paid for the infringement of it's patents from 'nearly every one of its competitors in the MRI industry including giant multi-nationals as Toshiba, Siemens, Shimadzu, Philips and GE'.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI History' (6).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI History' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Cine Sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
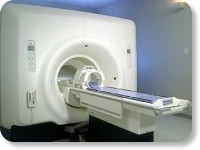
(Signa VH/i 3.0T)
With GE Healthcare
leading-edge technology in ultra-high-field imaging. The 3 T VH/i provides a platform for advanced applications in radiology, cardiology, psychology and psychiatry. Real-time image processing lets you acquire multislice whole brain images and map brain functions for research or surgical planning. And the 3 T Signa VH/i is flexible enough to provide clinicians with high performance they require. It can provide not only outstanding features in brain scanning and neuro-system research, but also a wide range of use in scanning breasts, extremities, the spine and the cardiovascular systems.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body
T/R quadrature head, T/R quadrature body, T/R phased array extremity (opt) SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE, FGRE, RF-spoiled GRE, FSE, Angiography: 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D phase contrast vascular IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, fast scan, multi slab, cine, localizer 100 Images/sec with Reflex100 MULTISLICE 100 Images/sec with Reflex100 2D 0.5-100mm in 0.1mm incremental 128x512 steps 32 phase encode H*W*D 260cm x 238cm x 265cm POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415, 3 phase ||
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled grad. Less than 0.14 L/hr liquid He | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Signa 3.0T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
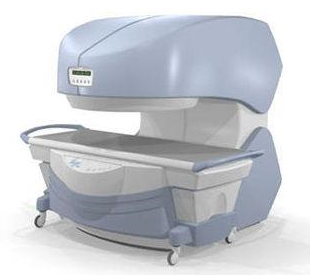
From
Millennium Technology Inc.
This open C-shaped MRI system eases patient comfort and technologist maneuverability. This low cost scanner is build for a wide range of applications. The Virgo™ patient table is detachable and moves on easy rolling castors. Able to accommodate patient weights up to 160 kg, the tabletop has a range of motion of 30 cm in the lateral direction and 90cm in the longitudinal direction. Images generated with this scanner can only be viewed (without data loss) on Millennium's proprietary viewing software.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head, Body, Neck, Knee, Shoulder,
Spine, Wrist, Breast, Extremity, Lumbar Spine, TMJ
IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |