 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'AIN' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Forces can result from the interaction of magnetic fields. Pulsed magnetic field gradients can interact with the m ain magnetic field during the MRI scan, to produce acoustic noise through the gradient coil.
Magnetic fields attract ferromagnetic objects with forces, which can be a lethal danger if one is hit by an unrestr ained object in flight. One could also be trapped between the magnet and a large unrestr ained ferromagnetic object or the object could damage the MRI machine.
Access control and personnel awareness are the best preventions of such accidents. The attraction mechanism for ferromagnetic objects is that the magnetic field magnetizes the iron. This induced magnetization reacts with the gradient of the magnetic field to produce an attraction toward the strongest area of the field. The details of this interaction are very dependent on the shape and composition of the attracted object. There is a very rapid increase of force as one approaches a magnet. There is also a torque or twisting force on objects, e.g. a long cylinder (such as a pen or an intracranial aneurysm clip) will tend to align along the magnet's field lines. The torque increases with field strength while the attraction increases with field gradient.
Depending on the magnetic saturation of the object, attraction is roughly proportional to object mass. Motion of conducting objects in magnetic fields can induce eddy currents that can have the effect of opposing the motion. See also Duty Cycle.
See also the related poll result: ' Most outages of your scanning system are caused by failure of' | |  | | • For this and other aspects of MRI safety see our InfoSheet about MRI Safety. | | | • Patient-related information is collected in our MRI Patient Information.
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | MRI Safety Resources | | | | |
|  |  |  |
| |
|
MultiHance® is a paramagnetic contrast agent for use in diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) of the liver and central nervous system. MultiHance® is a small molecular weight chelate, which tightly binds the Gd atom. The substance is excreted partly by the kidneys, partly by the biliary system, which is especially unique.
MultiHance® is indicated, for the detection of focal liver lesions in patients with known or suspected primary liver cancer (e.g. hepatocellular carcinoma) or metastatic disease.
MultiHance® is also indicated in brain MRI and spine MRI where it improves the detection of lesions and provides diagnostic information additional to that obt ained with unenhanced MRI.
Gd-BOPTA-enhanced MRA can provide superior vascular signal intensity and SNR, as compared with Gd-DTPA, due to its higher relaxivity, even at lower doses.
1 ml of solution MultiHance® cont ains: (0.5M) gadobenate dimeglumine 529 mg = gadobenic acid 334 mg + meglumine 195 mg. Viscosity at 37°C: 5.3 mPa
WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in patients with acute or chronic severe renal insufficiency (glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73m 2), or acute renal insufficiency of any severity due to the hepato-renal syndrome or in the perioperative liver transplantation period. Drug Information and Specification T1, predominantly positive enhancement r1=9.7, r2=12.5, B0=0.5 T PHARMACOKINETIC Extracellular, hepatobiliary PREPARATION Solution for injection DEVELOPMENT STAGE For sale PRESENTATION Vials of 5, 10, 15 and 20 mL, 50 and 100 mL Multipacks (Pharmacy Bulk Package)
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PACKAGE INSERT! Distribution Information TERRITORY TRADE NAME DEVELOPMENT
STAGE DISTRIBUTOR Australia MultiHance® for sale | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MultiHance®' (9).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MultiHance®' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(NSF) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is a rare and highly debilitating disorder that involves extensive thickening and hardening of the skin with fibrotic nodules and plaques.
MRI contrast media have very low side effects, but accumulating data indicate that gadolinium-based contrast agents increase the risk for the development of NSF among patients with severe renal insufficiency or renal dysfunction due to the hepato-renal syndrome or in the perioperative liver transplantation period.
Due to this reason, gadolinium contrast agents are now considered contr aindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate fewer than 30 mL/min/1.73m 2.
In these patients, avoid use of gadolinium-based contrast agents unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI).
Recognized or possibly associated factors for NSF:
•
high dose of erythropoietin;
•
high serum phosphate levels;
•
high serum calcium levels;
•
major surgery, infection, vascular event;
•
history of hypothyroidism;
When administering a gadolinium-based contrast agent, do not exceed the recommended dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the contrast medium from the body prior to any readminstration. Screen all patients for renal dysfunction by obt aining a history and/or laboratory tests.
See also Contrast Medium, Adverse Reaction, MRI Risks, MRI Safety, Ionic Intravenous Contrast Agents, Nonionic Intravenous Contrast Agents, and Contraindications.
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis' (13).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'AIN' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
In parallel MR imaging, a reduced data set in the phase encoding direction(s) of k-space is acquired to shorten acquisition time, combining the signal of several coil arrays. The spatial information related to the phased array coil elements is utilized for reducing the amount of conventional Fourier encoding.
First, low-resolution, fully Fourier-encoded reference images are required for sensitivity assessment. Parallel imaging reconstruction in the Cartesian case is efficiently performed by creating one aliased image for each array element using discrete Fourier transformation. The next step then is to create an full FOV image from the set of intermediate images.
Parallel reconstruction techniques can be used to improve the image quality with increased signal to noise ratio, spatial resolution, reduced artifacts, and the temporal resolution in dynamic MRI scans.
Parallel imaging algorithms can be divided into 2 m ain groups:
Image reconstruction produced by each coil ( reconstruction in the image dom ain, after Fourier transform): SENSE ( Sensitivity Encoding), PILS (Partially Parallel Imaging with Localized Sensitivity),
ASSET.
Reconstruction of the Fourier plane of images from the frequency signals of each coil ( reconstruction in the frequency dom ain, before Fourier transform): GRAPPA. Additional techniques include SMASH, SPEEDER™,
IPAT (Integrated Parallel Acquisition Techniques - derived of GRAPPA a k-space based technique) and mSENSE (an image based enhanced version of SENSE).
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Parallel Imaging Technique' (12).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
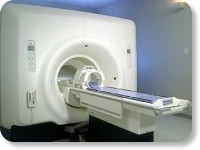
(Signa VH/i 3.0T)
With GE Healthcare
leading-edge technology in ultra-high-field imaging. The 3 T VH/i provides a platform for advanced applications in radiology, cardiology, psychology and psychiatry. Real-time image processing lets you acquire multislice whole brain images and map brain functions for research or surgical planning. And the 3 T Signa VH/i is flexible enough to provide clinicians with high performance they require. It can provide not only outstanding features in brain scanning and neuro-system research, but also a wide range of use in scanning breasts, extremities, the spine and the cardiovascular systems.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body
T/R quadrature head, T/R quadrature body, T/R phased array extremity (opt) SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE, FGRE, RF-spoiled GRE, FSE, Angiography: 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D phase contrast vascular IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, fast scan, multi slab, cine, localizer 100 Images/sec with Reflex100 MULTISLICE 100 Images/sec with Reflex100 2D 0.5-100mm in 0.1mm incremental 128x512 steps 32 phase encode H*W*D 260cm x 238cm x 265cm POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415, 3 phase ||
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled grad. Less than 0.14 L/hr liquid He | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Signa 3.0T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |