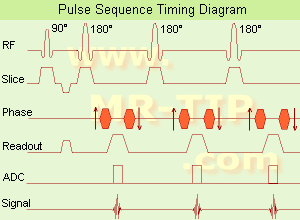
(FSE) In the
pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast
spin echo sequence with an
echo train length of 3 is illustrated.
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180°
rephasing pulses and multiple
echoes, changing the
phase encoding gradient for each
echo.
The
echo time TE may vary from
echo to
echo in the
echo train. The
echoes in the center of the
K-space (in the case of linear
k-space acquisition) mainly produce the type of image
contrast, whereas the periphery of
K-space determines the
spatial resolution. For example, in the middle of
K-space the late
echoes of
T2 weighted images are encoded. T1 or
PD contrast is produced from the early
echoes.
The benefit of this technique is that the scan duration with, e.g. a
turbo spin echo turbo factor /
echo train length of 9, is one ninth of the time. In
T1 weighted and
proton density weighted
sequences, there is a limit to how large the ETL can be (e.g. a usual ETL for
T1 weighted images is between 3 and 7). The use of large
echo train lengths with short TE results in
blurring and loss of
contrast. For this reason,
T2 weighted imaging profits most from this technique.
In
T2 weighted FSE images, both water and fat are hyperintense. This is because the succession of 180° RF pulses reduces the
spin spin interactions in fat and increases its T2
decay time. Fast
spin echo (FSE)
sequences have replaced conventional
T2 weighted spin echo sequences for most clinical applications. Fast
spin echo allows reduced acquisition times and enables
T2 weighted breath hold imaging, e.g. for applications in the upper abdomen.
In case of the acquisition of 2
echoes this type of a sequence is named
double fast spin echo /
dual echo sequence, the first
echo is usually density and the
second echo is
T2 weighted image. Fast
spin echo images are more
T2 weighted, which makes it difficult to obtain true
proton density weighted images. For
dual echo imaging with density weighting, the TR should be kept between 2000 - 2400 msec with a short ETL (e.g., 4).
Other terms for this technique are:
Turbo Spin Echo
Rapid Imaging
Spin Echo,
Rapid
Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition
Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes