 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Low Field MRI' found in 1 term [ ] and 7 definitions [ ] and 7 definitions [ ], (+ 17 Boolean[ ], (+ 17 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 25) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2]  [3 4 5] [3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Low Field MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
AI analysis finds younger AFib patients benefit from MRI-guided ablation treatments
Friday, 25 August 2023 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Theranostic nano-platform for MRI-guided synergistic therapy against breast cancer
Monday, 26 September 2022 by phys.org |  |  |
Magnetic seeds used to heat and kill cancer
Tuesday, 1 February 2022 by www.sciencedaily.com |  |  |
What is the effect of MRI with targeted biopsies on the rate of patients discontinuing active surveillance? A reflection of the use of MRI in the PRIAS study
Thursday, 8 April 2021 by www.docwirenews.com |  |  |
Modeling of Active Shimming of Metallic Needles for Interventional MRI
Monday, 29 June 2020 by pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Confirmatory Biopsy for Initiating Active Surveillance of Prostate Cancer
Wednesday, 11 September 2019 by jamanetwork.com |  |  |
FDA clears ViewRay's next-gen, MRI-guided radiation therapy device
Tuesday, 28 February 2017 by www.fiercebiotech.com |  |  |
Siemens, U. of Twente Biopsy Robot Promises Greater Precision, Less Cost
Friday, 22 January 2016 by www.meddeviceonline.com |  |  |
Magnetic resonance-guided motorized transcranial ultrasound system for blood-brain barrier permeabilization along arbitrary trajectories in rodents
Thursday, 24 December 2015 by www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
New MRI-Guided Catheter Shows Major Potential for Stroke Treatment
Tuesday, 29 December 2015 by www.radiology.ucsf.edu |  |  |
Polish study on MRI-ultrasound for targeted prostate biopsy wins CEM award
Tuesday, 12 November 2013 by medicalxpress.com |  |  |
C4 Imaging Announces FDA 510(k) Clearance of its Positive-Signal MRI Marker - Sirius™
Friday, 6 December 2013 by www.digitaljournal.com |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|

It is important to remember when working around a superconducting magnet that the magnetic field is always on. Under usual working conditions the field is never turned off. Attention must be paid to keep all ferromagnetic items at an adequate distance from the magnet. Ferromagnetic objects which came accidentally under the influence of these strong magnets can injure or kill individuals in or nearby the magnet, or can seriously damage every hardware, the magnet itself, the cooling system, etc..
See MRI resources Accidents.
The doors leading to a magnet room should be closed at all times except when entering or exiting the room. Every person working in or entering the magnet room or adjacent rooms with a magnetic field has to be instructed about the dangers. This should include the patient, intensive-care staff, and maintenance-, service- and cleaning personnel, etc..
The 5 Gauss limit defines the 'safe' level of static magnetic field exposure. The value of the absorbed dose is fixed by the authorities to avoid heating of the patient's tissue and is defined by the specific absorption rate.
Leads or wires that are used in the magnet bore during imaging procedures, should not form large-radius wire loops. Leg-to-leg and leg-to-arm skin contact should be prevented in order to avoid the risk of burning due to the generation of high current loops if the legs or arms are allowed to touch. The patient's skin should not be in contact with the inner bore of the magnet.
The outflow from cryogens like liquid helium is improbable during normal operation and not a real danger for patients.
The safety of MRI contrast agents is tested in drug trials and they have a high compatibility with very few side effects. The variations of the side effects and possible contraindications are similar to X-ray contrast medium, but very rare. In general, an adverse reaction increases with the quantity of the MRI contrast medium and also with the osmolarity of the compound.
See also 5 Gauss Fringe Field, 5 Gauss Line, Cardiac Risks, Cardiac Stent, dB/dt, Legal Requirements, Low Field MRI, Magnetohydrodynamic Effect, MR Compatibility, MR Guided Interventions, Claustrophobia, MRI Risks and Shielding. | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Safety' (42).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Safety' (13).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Open MRI scanners have been developed for people who are anxious or obese or for examination of small parts of the body, such as the extremities ( knee, shoulder). In addition, some systems offer imaging in different positions and sequences of movements.
The basic technology of an open MRI machine is similar to that of a traditional MRI device.
The major difference for the patient is that instead of lying in a narrow tunnel, the imaging table has more space around the body so that the magnet does not completely surround the person being tested.
Types of constructions:
•
Semi open high field MRI scanners provide an ultra short bore (tunnel) and widely flared ends. In this type of MRI systems, patients lie with the head in the space outside the bore, if for example the hips are examined.
•
Open low field MRI machines have often a wide open design, e.g. an open C-arm scanner is shaped like two large discs separated by a large pillar. Patients have an open sided feeling and more space around them allows a wider range of positions.
•
Advanced open MRI scanners combine the advantages of both, the high field strength, newest gradient technology and wide open design. Even scans of patients in upright, weight-bearing positions are possible (e.g. Upright™ MRI formerly Stand-Up MRI).
Difficulties with a traditional MRI scan include claustrophobia and patient size or, for health related reasons, patients who are not able to receive this type of diagnostic test. The MRI unit is a limited space, and some patients may be too large to fit in a narrow tunnel. In addition, weight limits can restrict the use of some scanners. The open MRI magnet has become the best option for those patients.
All of the highest resolution MRI scanners are tunnels and tend to accentuate the claustrophobic reaction. While patients may find the open MRI scanners easier to tolerate, some machines use a lower field magnet and generates lower image quality or have longer scan time. The better performance of an advanced open MRI scanner allows good image quality caused by the higher signal to noise ratio with maximum patient comfort.
See also Claustrophobia, MRI scan and Knee MRI. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Open MRI' (37).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Open MRI' (16).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Low Field MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|

From GE Healthcare;
The Signa SP 0.5T™ is an open MRI magnet that is designed for use in interventional radiology and intra-operative imaging. The vertical gap configuration increases patient positioning options, improves patient observation, and al lows continuous access to the patient during imaging.
The magnet enclosure also incorporates an intercom, patient observation video camera, laser patient alignment lights, and task lighting in the imaging volume.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Integrated transmit and receive body coil; optional rotational body coil, head; other coils optional; open architecture makes system compatible with a wide selection of coilsarray Standard: SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE and SPGR, 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D FSE, 2D/3D FGRE and FSPGR, SSFP, FLAIR, EPI, optional: 2D/3D Fiesta, true chem sat, fat/water separation, single shot diffusion EPI IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF TR 1.3 to 12000 msec in increments of 1 msec TE 0.4 to 2000 msec in increments of 1 msec 2D: 1.4mm - 20mm 3D: 0.2mm - 20mm POWER REQUIREMENTS 200 - 480, 3-phase | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Signa SP 0.5T™ Open Configuration' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
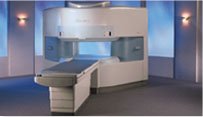
From Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc.;
the AIRIS made its debut in 1995. Hitachi fol lowed up with the AIRIS II system, which has proven equally successfully. 'All told, Hitachi has installed more than 1,000 MRI systems in the U.S., holding more than 17 percent of the total U.S. MRI installed base, and more than half of the installed base of open MR systems,' says Antonio Garcia, Frost and Sullivan industry research analyst.
Now Altaire employs a blend of innovative Hitachi features called VOSI™ technology, optimizing each sub-system's performance in concert with the
other sub-systems, to give the seamless mix of high- field performance
and the patient comfort, especially for claustrophobic patients, of open MR systems.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
DualQuad T/R Body Coil, MA Head, MA C-Spine, MA Shoulder, MA Wrist, MA CTL Spine, MA Knee, MA TMJ, MA Flex Body (3 sizes), Neck, small and large Extremity, PVA (WIP), Breast (WIP), Neurovascular (WIP), Cardiac (WIP) and MA Foot//Ankle (WIP)
SE, GE, GR, IR, FIR, STIR, ss-FSE, FSE, DE-FSE/FIR, FLAIR, ss/ms-EPI, ss/ms EPI- DWI, SSP, MTC, SE/GE-EPI, MRCP, SARGE, RSSG, TRSG, BASG, Angiography: CE, PC, 2D/3D TOF
IMAGING MODES
Single, multislice, volume study
TR
SE: 30 - 10,000msec GE: 3.6 - 10,000msec IR: 50 - 16,700msec FSE: 200 - 16,7000msec
TE
SE : 8 - 250msec IR: 5.2 -7,680msec GE: 1.8 - 2,000 msec FSE: 5.2 - 7,680
0.05 sec/image (256 x 256)
2D: 2 - 100 mm; 3D: 0.5 - 5 mm
Level Range: -2,000 to +4,000
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE
Water-cooled
3.1 m lateral, 3.6 m vertical
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Altaire™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |