 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Metal Artifact' found in 1 term [ ] and 1 definition [ ] and 1 definition [ ], (+ 4 Boolean[ ], (+ 4 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 6) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Metal Artifact ' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| Metal Artifact |  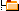 |
| |
|
Quick Overview
NAME
Metal, susceptibility
Ferromagnetic metal will cause a magnetic field inhomogeneity, which in turn causes a local signal void, often accompanied by an area of high signal intensity, as well as a distortion of the image.
They create their own magnetic field and dramatically alter precession frequencies of protons in the adjacent tissues. Tissues adjacent to ferromagnetic components become influenced by the induced magnetic field of the metal hardware rather than the parent field and, therefore, either fail to precess or do so at a different frequency and hence do not generate useful signal. Two components contribute to susceptibility artifact, induced magnetism in the ferromagnetic component itself and induced magnetism in protons adjacent to the component. Artifacts from metal may have varied appearances on MRI scans due to different type of metal or configuration of the piece of metal.
The biocompatibility of metallic alloys, stainless steel, cobalt chrome and titanium alloy is based on the presence of a constituent element within the alloy that has the ability to form an adherent oxide coating that is stable, chemically inert and hence biocompatible. In relation to imaging titanium alloys are less ferromagnetic than both cobalt and stainless steel, induce less susceptibility artifact and result in less marked image degradation.

Image Guidance
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Metal Artifact':    | | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
Materials with magnetic susceptibility cause this artifact. There are in general three kinds of materials with magnetic susceptibility: ferromagnetic materials (iron, nickel etc.) with a strong influence and paramagnetic/diamagnetic (aluminium, platinum etc./gold, water, most organic compounds etc.) materials with a minimal/non influence on magnetic fields. In MRI, susceptibility artifacts are caused for example by medical devices in or near the magnetic field or by implants of the patient. These materials with magnetic susceptibility distort the linear magnetic field gradients, which results in bright areas (misregistered signals) and dark areas (no signal) nearby the magnetic material.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Susceptibility Artifact' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
An image artifact is a structure not normally present but visible as a result of a limitation or malfunction in the hardware or software of the MRI device, or in other cases a consequence of environmental influences as heat or humidity or it can be caused by the human body (blood flow, implants etc.). The knowledge of MRI artifacts (brit. artefacts) and noise producing factors is important for continuing maintenance of high image quality. Artifacts may be very noticeable or just a few pixels out of balance but can give confusing artifactual appearances with pathology that may be misdiagnosed.
Changes in patient position, different pulse sequences, metallic artifacts, or other imaging variables can cause image distortions, which can be reduced by the operator; artifacts due to the MR system may require a service engineer.
Many types of artifacts may occur in magnetic resonance imaging. Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging are typically classified as to their basic principles, e.g.:
•
Physiologic (motion, flow)
•
Hardware (electromagnetic spikes, ringing)
Several techniques are developed to reduce these artifacts (e.g. respiratory compensation, cardiac gating, eddy current compensation) but sometimes these effects can also be exploited, e.g. for flow measurements.
See also the related poll result: ' Most outages of your scanning system are caused by failure of'
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Artifact' (166).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Metal Artifact ' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Gastrointestinal (GI) superparamagnetic contrast agents are used in MRI to improve the visualization of e.g., the intestinal tract, the pancreas (see MRCP), etc.
Disadvantages are susceptibility artifacts e.g., dependent on delayed imaging or large volumes resulting in artifacts in the colon and distal small bowel loops related to higher concentration of the particles and absorption of the fluid.
Different types of MRI gastrointestinal superparamagnetic contrast agents:
•
Magnetite albumin microsphere
Usually gastrointestinal superparamagnetic contrast media consist of small iron oxide crystals (ferrites), which produce a signal reduction in the stomach and bowel after oral administration. The T2 shortening caused by these particles is produced from the local magnetic field inhomogeneities associated with the large magnetic moments of superparamagnetic particles. Ferrites are iron oxides of the general formula Fe203.MO, where M is a divalent metal ion and may be mixed with Fe3O4 in different preparations.
Ferrites can produce symptoms of nausea after oral administration, as well as flatulence and a transient rise in serum iron. Embedding in inert substances reduce side effects by decreasing the absorption and interaction with body tissues. Combining these contrast materials with polymers such as polyethylene glycol or cellulose, or with sugars such as dextrose, results in improved T1 and/or T2 relaxivity compared with that of the contrast agent alone.
See also Negative Oral Contrast Agents, Gastrointestinal Diamagnetic Contrast Agents, Relaxivity, and Combination Oral Contrast Agents. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Gastrointestinal Superparamagnetic Contrast Agents' (6).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Metal dental work can cause, depending of the material, an associated artifact distant from the source. There is no risk for the patient but for good MRI quality should every removable dental work be removed. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Dental Work' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 6) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |