 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Multi Shot Technique' found in 1 term [ ] and 0 definition [ ] and 0 definition [ ], (+ 9 Boolean[ ], (+ 9 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 10) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |  | | |  |  |  |
| |
|
When a multi shot technique is applied, each shot will have its own effect on the prepulse, with a scan time increase. Multiple shots allow a shorter IR delay but at the cost of increased scan time.
In multi shot technique (also called mosaic imaging), a group of samples, which are contiguous in k space are acquired in the same sequence repetition. The phase encoding steps or profiles are split into 'shots' (sub-acquisitions). The shot interval is the time between the shots. Usually kept as short as possible. Because the acquisitions are divided into different shots, each shot will have less T1 variation, thereby increasing T1 contrast. Two excitations, each requiring the data for one half of k-space, are the simplest variation of multi shot techniques (e.g. positive versus negative phase encoding).
The alternative to this mosaic strategy for multi shot EPI is interleaving. In interleaved sequences, each repetition acquires every nth (n is the number of shots) line in k-space and for the complete raw data set the various repetition data are interlaced.
See also Single Shot Technique. | |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Multi Shot Technique':    | | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
•
In the 1930's, Isidor Isaac Rabi (Columbia University) succeeded in detecting and measuring single states of rotation of atoms and molecules, and in determining the mechanical and magnetic moments of the nuclei.
•
Felix Bloch (Stanford University) and Edward Purcell (Harvard University) developed instruments, which could measure the magnetic resonance in bulk material such as liquids and solids. (Both honored with the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1952.) [The birth of the NMR spectroscopy]
•
In the early 70's, Raymond Damadian (State University of New York) demonstrated with his NMR device, that there are different T1 relaxation times between normal and abnormal tissues of the same type, as well as between different types of normal tissues.
•
In 1973, Paul Lauterbur (State University of New York) described a new imaging technique that he termed Zeugmatography. By utilizing gradients in the magnetic field, this technique was able to produce a two-dimensional image (back-projection). (Through analysis of the characteristics of the emitted radio waves, their origin could be determined.) Peter Mansfield further developed the utilization of gradients in the magnetic field and the mathematically analysis of these signals for a more useful imaging technique. (Paul C Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield were awarded with the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medicine.)
•
1977/78: First images could be presented.
A cross section through a finger by Peter Mansfield and Andrew A. Maudsley.
Peter Mansfield also could present the first image through the abdomen.
•
In 1977, Raymond Damadian completed (after 7 years) the first MR scanner (Indomitable). In 1978, he founded the FONAR Corporation, which manufactured the first commercial MRI scanner in 1980. Fonar went public in 1981.
•
1981: Schering submitted a patent application for Gd-DTPA dimeglumine.
•
1982: The first 'magnetization-transfer' imaging by Robert N. Muller.
•
In 1983, Toshiba obtained approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan for the first commercial MRI system.
•
1986: Jürgen Hennig, A. Nauerth, and Hartmut Friedburg (University of Freiburg) introduced RARE (rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement) imaging. Axel Haase, Jens Frahm, Dieter Matthaei, Wolfgang Haenicke, and Dietmar K. Merboldt (Max-Planck-Institute, Göttingen) developed the FLASH ( fast low angle shot) sequence.
•
1988: Schering's MAGNEVIST gets its first approval by the FDA.
•
In 1991, fMRI was developed independently by the University of Minnesota's Center for Magnetic Resonance Research (CMRR) and Massachusetts General Hospital's (MGH) MR Center.
•
From 1992 to 1997 Fonar was paid for the infringement of it's patents from 'nearly every one of its competitors in the MRI industry including giant multi-nationals as Toshiba, Siemens, Shimadzu, Philips and GE'.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI History' (6).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI History' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
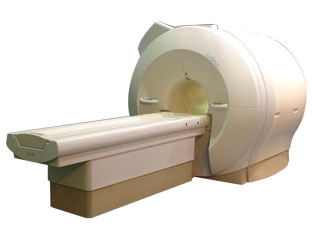
'Next generation MRI system 1.5T CHORUS developed by ISOL Technology is optimized for both clinical diagnostic imaging and for research development.
CHORUS offers the complete range of feature oriented advanced imaging techniques- for both clinical routine and research. The compact short bore magnet, the patient friendly design and the gradient technology make the innovation to new degree of perfection in magnetic resonance.'
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Spin Echo, Gradient Echo, Fast Spin Echo,
Inversion Recovery ( STIR, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery), FLASH, FISP, PSIF, Turbo Flash ( MPRAGE ),TOF MR Angiography, Standard echo planar imaging package (SE-EPI, GE-EPI), Optional:
Advanced P.A. Imaging Package (up to 4 ch.), Advanced echo planar imaging package,
Single Shot and Diffusion Weighted EPI, IR/FLAIR EPI
STRENGTH
20 mT/m (Upto 27 mT/m)
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'CHORUS 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Ultrasound imaging is the primary fetal monitoring modality during pregnancy, nevertheless fetal MRI is increasingly used to image anatomical regions and structures difficult to see with sonography. Given its long record of safety, utility, and cost-effectiveness, ultrasound will remain the modality of first choice in fetal screening. However, MRI is beginning to fill a niche in situations where ultrasound does not provide enough information to diagnose abnormalities before the baby's birth. Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetus provides multiplanar views also in sub-optimal positions, better characterization of anatomic details of e.g. the fetal brain, and information for planning the mode of delivery and airway management at birth.
Indications:
•
Examinations of the placenta
Modern fetal MRI requires no sedatives or muscle relaxants to control fetal movement. Ultrafast MRI techniques (e.g., single shot techniques like Half Fourier Acquisition Single shot Turbo spin Echo HASTE) enable images to be acquired in less than one second to eliminate fetal motion. Such technology has led to increased usage of fetal MRI, which can lead to earlier diagnosis of conditions affecting the baby and has proven useful in planning fetal surgery and designing postnatal treatments. As MR technology continues to improve, more advances in the prenatal diagnosis and treatment of fetal abnormalities are to expect. More advances in in-utero interventions are likely as well. Eventually, fetal MRI may replace even some prenatal tests that require invasive procedures such as amniocentesis.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Fetal Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fetal MRI' (5).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Fetal MRI' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Advances in medical imaging enable visualization of white matter tracts in fetuses
Wednesday, 12 May 2021 by www.eurekalert.or |  |  |
Fetal CMR Detects Congenital Heart Defects, Changes Treatment Decisions
Monday, 29 March 2021 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
MRI scans more precisely define and detect some abnormalities in unborn babies
Friday, 12 March 2021 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum in Fetuses: Frontal Horns and Cavum Septi Pellucidi Are Clues to Earlier Diagnosis
Monday, 29 June 2020 by pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
MRI helps predict preterm birth
Tuesday, 15 March 2016 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
3-T MRI advancing on ultrasound for imaging fetal abnormalities
Monday, 20 April 2015 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Babies benefit from pioneering 'miniature' MRI scanner in Sheffield
Friday, 24 January 2014 by www.telegraph.co.uk |  |  |
Ultrasensitive Detector Pinpoints Big Problem in Tiny Fetal Heart
Tuesday, 6 April 2010 by www.sciencedaily.com |  |  |
Real-time MRI helps doctors assess beating heart in fetus
Thursday, 29 September 2005 by www.eurekalert.org |
|
| |
|  | |  |  | |  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 10) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |