 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Pulse Sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
( BOLD) In MRI the changes in blood oxygenation level are visible. Oxyhaemoglobin (the principal haemoglobin in arterial blood) has no substantial magnetic properties, but deoxyhaemoglobin (present in the draining veins after the oxygen has been unloaded in the tissues) is strongly paramagnetic. It can thus serve as an intrinsic paramagnetic contrast agent in appropriately performed brain MRI. The concentration and relaxation properties of deoxyhaemoglobin make it a susceptibility , e.g. T2 relaxation effective contrast agent with little effect on T1 relaxation.
During activation of the brain, the oxygen consumption of the local tissue increase by approximately 5% with that the oxygen tension will decrease. As a consequence, after a short period of time vasodilatation occurs, resulting in a local increase of blood volume and flow by 20 - 40%. The incommensurate change in local blood flow and oxygen extraction increases the local oxygen level.
By using T2 weighted gradient echo EPI sequences, which are highly susceptibility sensitive and fast enough to capture the three-dimensional nature of activated brain areas will show an increase in signal intensity as oxyhaemoglobin is diamagnetic and deoxyhaemoglobin is paramagnetic. Other MR pulse sequences, such as spoiled gradient echo pulse sequences are also used.
As the effects are subtle and of the order of 2% in 1.5 T MR imaging, sophisticated methodology, paradigms and data analysis techniques have to be used to consistently demonstrate the effect.
As the BOLD effect is due to the deoxygenated blood in the draining veins, the spatial localization of the region where there is increased blood flow resulting in decreased oxygen extraction is not as precisely defined as the morphological features in MRI. Rather there is a physiological blurring, and is estimated that the linear dimensions of the physiological spatial resolution of the BOLD phenomenon are around 3 mm at best. | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Pulse Sequence' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
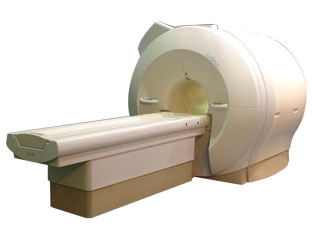
'Next generation MRI system 1.5T CHORUS developed by ISOL Technology is optimized for both clinical diagnostic imaging and for research development.
CHORUS offers the complete range of feature oriented advanced imaging techniques- for both clinical routine and research. The compact short bore magnet, the patient friendly design and the gradient technology make the innovation to new degree of perfection in magnetic resonance.'
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Spin Echo, Gradient Echo, Fast Spin Echo,
Inversion Recovery ( STIR, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery), FLASH, FISP, PSIF, Turbo Flash ( MPRAGE ),TOF MR Angiography, Standard echo planar imaging package (SE-EPI, GE-EPI), Optional:
Advanced P.A. Imaging Package (up to 4 ch.), Advanced echo planar imaging package,
Single Shot and Diffusion Weighted EPI, IR/FLAIR EPI
STRENGTH
20 mT/m (Upto 27 mT/m)
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'CHORUS 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
This method synchronize the heartbeat with the beginning of the TR, whereat the r wave is used as the trigger. Cardiac gating times the acquisition of MR data to physiological motion in order to minimize motion artifacts. ECG gating techniques are useful whenever data acquisition is too slow to occur during a short fraction of the cardiac cycle.
Image blurring due to cardiac-induced motion occurs for imaging times of above approximately 50 ms in systole, while for imaging during diastole the critical time is of the order of 200-300 ms. The acquisition of an entire image in this time is only possible with using ultrafast MR imaging techniques. If a series of images using cardiac gating or real-time echo planar imaging EPI are acquired over the entire cardiac cycle, pixel-wise velocity and vascular flow can be obtained.
In simple cardiac gating, a single image line is acquired in each cardiac cycle. Lines for multiple images can then be acquired successively in consecutive gate intervals. By using the standard multiple slice imaging and a spin echo pulse sequence, a number of slices at different anatomical levels is obtained. The repetition time (TR) during a ECG-gated acquisition equals the RR interval, and the RR interval defines the minimum possible repetition time (TR). If longer TRs are required, multiple integers of the RR interval can be selected. When using a gradient echo pulse sequence, multiple phases of a single anatomical level or multiple slices at different anatomical levels can be acquired over the cardiac cycle.
Also called cardiac triggering. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Cardiac Gating' (15).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Pulse Sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Carr Purcell Meiboom Gill Sequence' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Pulse Sequence' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Cine sequences used in cardiovascular MRI are collection of images (usually at the same spatial location) covering of one full period of cardiac cycle or over several periods in order to obtain complete coverage.
The pulse sequence used, is either a standard gradient echo pulse sequence, a segmented data acquisition, a gradient echo EPI sequence or a gradient echo with balanced gradient waveform.
In cardiac gating studies it is possible to assign consecutive lines either to different images, yielding a multiphase sequence with as many images as lines, or the lines are grouped together into segments and assigned to the same image. The overall time to acquire such a segment has to be small compared to the RR-interval of the cardiac cycle, i. e. 50 ms, and hence contains typically 8 to 16 image lines.
This strategy is called segmented data acquisition, and has the advantage of reducing overall imaging time for cardiac images so that they can be acquired within a breath hold, but obviously decreasing the temporal resolution of each individual image.
This method shows dynamic processes, such as the ejection of blood out of the heart into the aorta, by means of fast imaging and displaying the resulting images in a sequential-loop, the impression of a real-time movie is generated. Ejection fractions and stroke volumes calculated from these cine MRI images in different cardiac axes have been shown to be more accurate than any other imaging modality. See also Cardiac Gating. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Cine Sequence' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |