 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Rise Time' found in 1 term [ ] and 3 definitions [ ] and 3 definitions [ ], (+ 9 Boolean[ ], (+ 9 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 13) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Rise Time' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| Rise Time |  |
| |
|
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Rise Time':    | | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Slew Rate' (8).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Slew Rate' (1).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Echo Spacing' (6).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Rise Time' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
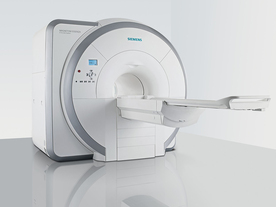
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2007.
The MAGNETOM Essenza is designed to combine high system performance with simple installation and power requirements to provide optimal operating costs for limited budgets. The standard system has up to 25 integrated coil elements and 8 independent radio frequency channels. Tim allows the combination of up to 4 different coils that reduce patient and coil repositioning.
The 1.5 Tesla system is designated for a complete range of clinical applications, including neurology, orthopedics, body imaging, angiography, cardiology, breast imaging, oncology and pediatric MRI.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra-short bore
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck, and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle, TMJ optional.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
8, 16
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
4350 kg in operation
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
145 x 226 x 216 cm
COOLING SYSTEM
Water; single cryogen, 2 stage refrigeration
30 mT/m, 300 msec to 10 mT/m
Passive, active; first order standard
second order optional
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 45 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
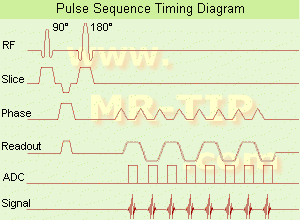
(EPI) Echo planar imaging is one of the early magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like diffusion, perfusion, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other sequences acquire one k-space line at each phase encoding step. When the echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all k-space lines are measured in one repetition time) of a gradient echo or spin echo sequence (see single shot technique) with an acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
The pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an echo planar imaging sequence from spin echo type with eight echo train pulses. (See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the MRI scanner like much larger gradient amplitudes. The scan time is dependent on the spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied gradient fields and the time the machine needs to ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is water fat shift in the phase encoding direction due to phase accumulations. To minimize water fat shift (WFS) in the phase direction fat suppression and a wide bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the flat top of the gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner hardware, in particular on gradient strengths, gradient switching times, and receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Echo Planar Imaging' (19).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Echo Planar Imaging' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 13) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |