 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Single Shot Technique' found in 1 term [ ] and 8 definitions [ ] and 8 definitions [ ], (+ 6 Boolean[ ], (+ 6 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 11 - 15 (of 15) Result Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2]  [3] [3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Single Shot Technique' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
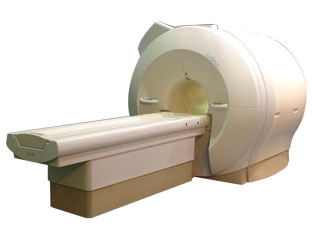
'Next generation MRI system 1.5T CHORUS developed by ISOL Technology is optimized for both clinical diagnostic imaging and for research development.
CHORUS offers the complete range of feature oriented advanced imaging techniques- for both clinical routine and research. The compact short bore magnet, the patient friendly design and the gradient technology make the innovation to new degree of perfection in magnetic resonance.'
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Spin Echo, Gradient Echo, Fast Spin Echo,
Inversion Recovery ( STIR, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery), FLASH, FISP, PSIF, Turbo Flash ( MPRAGE ),TOF MR Angiography, Standard echo planar imaging package (SE-EPI, GE-EPI), Optional:
Advanced P.A. Imaging Package (up to 4 ch.), Advanced echo planar imaging package,
Single Shot and Diffusion Weighted EPI, IR/FLAIR EPI
STRENGTH
20 mT/m (Upto 27 mT/m)
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Lung Imaging' (7).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Lung Imaging' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Chest MRI a viable alternative to chest CT in COVID-19 pneumonia follow-up
Monday, 21 September 2020 by www.healthimaging.com |  |  |
CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Corona virus (2019-nCoV)
Tuesday, 4 February 2020 by pubs.rsna.org |  |  |
Polarean Imaging Phase III Trial Results Point to Potential Improvements in Lung Imaging
Wednesday, 29 January 2020 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Low Power MRI Helps Image Lungs, Brings Costs Down
Thursday, 10 October 2019 by www.medgadget.com |  |  |
Chest MRI Using Multivane-XD, a Novel T2-Weighted Free Breathing MR Sequence
Thursday, 11 July 2019 by www.sciencedirect.co |  |  |
Researchers Review Importance of Non-Invasive Imaging in Diagnosis and Management of PAH
Wednesday, 11 March 2015 by lungdiseasenews.com |  |  |
New MRI Approach Reveals Bronchiectasis' Key Features Within the Lung
Thursday, 13 November 2014 by lungdiseasenews.com |  |  |
MRI techniques improve pulmonary embolism detection
Monday, 19 March 2012 by medicalxpress.com |
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Half Fourier Acquisition Single Shot Turbo Spin Echo' (5).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Single Shot Technique' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(SENSE) A MRI technique for relevant scan time reduction. The spatial information related to the coils of a receiver array are utilized for reducing conventional Fourier encoding. In principle, SENSE can be applied to any imaging sequence and k-space trajectories. However, it is particularly feasible for Cartesian sampling schemes. In 2D Fourier imaging with common Cartesian sampling of k-space sensitivity encoding by means of a receiver array enables to reduce the number of Fourier encoding steps.
SENSE reconstruction without artifacts relies on accurate knowledge of the individual coil sensitivities. For sensitivity assessment, low-resolution, fully Fourier-encoded reference images are required, obtained with each array element and with a body coil.
The major negative point of parallel imaging techniques is that they diminish SNR in proportion to the numbers of reduction factors.
R is the factor by which the number of k-space samples is reduced. In standard Fourier imaging reducing the sampling density results in the reduction of the FOV, causing aliasing. In fact, SENSE reconstruction in the Cartesian case is efficiently performed by first creating one such aliased image for each array element using discrete Fourier transformation (DFT).
The next step then is to create a full-FOV image from the set of intermediate images. To achieve this one must undo the signal superposition underlying the fold-over effect. That is, for each pixel in the reduced FOV the signal contributions from a number of positions in the full FOV need to be separated. These positions form a Cartesian grid corresponding to the size of the reduced FOV.
The advantages are especially true for contrast-enhanced MR imaging such as
dynamic liver MRI (liver imaging) ,
3 dimensional magnetic resonance angiography (3D MRA), and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreaticography ( MRCP).
The excellent scan speed of SENSE allows for acquisition of two separate sets of hepatic MR images within the time regarded as the hepatic arterial-phase (double arterial-phase technique) as well as that of multidetector CT.
SENSE can also increase the time efficiency of spatial signal encoding in 3D MRA. With SENSE, even ultrafast (sub second) 4D MRA can be realized.
For MRCP acquisition, high-resolution 3D MRCP images can be constantly provided by SENSE. This is because SENSE resolves the presence of the severe motion artifacts due to longer acquisition time. Longer acquisition time, which results in diminishing image quality, is the greatest problem for 3D MRCP imaging.
In addition, SENSE reduces the train of gradient echoes in combination with a faster k-space traversal per unit time, thereby dramatically improving the image quality of single shot echo planar imaging (i.e. T2 weighted, diffusion weighted imaging). | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Sensitivity Encoding' (12).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
The definition of imaging is the visual representation of an object. Medical imaging began after the discovery of x-rays by Konrad Roentgen 1896. The first fifty years of radiological imaging, pictures have been created by focusing x-rays on the examined body part and direct depiction onto a single piece of film inside a special cassette. The next development involved the use of fluorescent screens and special glasses to see x-ray images in real time.
A major development was the application of contrast agents for a better image contrast and organ visualization. In the 1950s, first nuclear medicine studies showed the up-take of very low-level radioactive chemicals in organs, using special gamma cameras. This medical imaging technology allows information of biologic processes in vivo. Today, PET and SPECT play an important role in both clinical research and diagnosis of biochemical and physiologic processes. In 1955, the first x-ray image intensifier allowed the pick up and display of x-ray movies.
In the 1960s, the principals of sonar were applied to diagnostic imaging. Ultrasonic waves generated by a quartz crystal are reflected at the interfaces between different tissues, received by the ultrasound machine, and turned into pictures with the use of computers and reconstruction software. Ultrasound imaging is an important diagnostic tool, and there are great opportunities for its further development. Looking into the
future, the grand challenges include targeted contrast agents, real-time 3D ultrasound imaging, and molecular imaging.
Digital imaging techniques were implemented in the 1970s into conventional fluoroscopic image intensifier and by Godfrey Hounsfield with the first computed tomography. Digital images are electronic snap shots sampled and mapped as a grid of dots or pixels. The introduction of x-ray CT revolutionised medical imaging with cross sectional images of the human body and high contrast between different types of soft tissue. These developments were made possible by analog to digital converters and computers. The multislice spiral CT technology has expands the clinical applications dramatically.
The first MRI devices were tested on clinical patients in 1980. The spread of CT machines is the spur to the rapid development of MRI imaging and the introduction of tomographic imaging techniques into diagnostic nuclear medicine. With technological improvements including higher field strength, more open MRI magnets, faster gradient systems, and novel data-acquisition techniques, MRI is a real-time interactive imaging modality that provides both detailed structural and functional information of the body.
Today, imaging in medicine has advanced to a stage that was inconceivable 100 years ago, with growing medical imaging modalities:
•
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
•
Positron emission tomography (PET)
All this type of scans are an integral part of modern healthcare.
Because of the rapid development of digital imaging modalities, the increasing need for an efficient management leads to the widening of radiology information systems (RIS) and archival of images in digital form in picture archiving and communication systems (PACS).
In telemedicine, healthcare professionals are linked over a computer network. Using cutting-edge computing and communications technologies, in videoconferences, where audio and visual images are transmitted in real time, medical images of MRI scans, x-ray examinations, CT scans and other pictures are shareable.
See also Hybrid Imaging.
See also the related poll results: ' In 2010 your scanner will probably work with a field strength of', ' MRI will have replaced 50% of x-ray exams by' | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Medical Imaging' (20).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Medical Imaging' (81).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | previous 11 - 15 (of 15) Result Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2]  [3] [3] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |