 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Upright MRI' found in 0 term [ ] and 2 definitions [ ] and 2 definitions [ ], (+ 4 Boolean[ ], (+ 4 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 6) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Upright MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|

The company is a leading manufacturer and developer of magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) scanners.
The Patient Friendly MRI Company, formed in 1978, is engaged in the business of inventing, manufacturing, selling and servicing magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) scanners. FONAR is the oldest MRI company in the world. After receiving hundreds of millions in a windfall from protecting their MRI patents, they made a MRI scanner that no other MRI manufacturer has. One that the patient stands in and they call Indomitable, the Stand-Up MRI. Patients like it because it is the least claustrophobic, most comfortable MRI on the market. Doctors like it because of its superior image quality and for the first time, the patient can be scanned in the weight-bearing position, or the position of pain or symptom. In October of 2004, the company changed the product name of the Stand-Up MRI to the Upright MRI. Fonar introduced the first "open" MRI scanner in 1980 and is the originator of the iron-core nonsuperconductive and permanent magnet technology.
MRI Scanners:
- 0.6T:
•
QUAD™ 12000 - Its 19-inch gap and Whisper Gradients™ make it extraordinarily spacious, quiet and comfortable. With its signal to noise advantage of 0.6 T and its comprehensive array of Organ-Specific™ receiver coils, the QUAD™ 12000 provides high-speed, high resolution and high contrast scanning.
Product Specification
•
OR 360°™ - cleared for marketing by the FDA in March 2000, 360° access to the patient. A dual-purpose scanner, it can be used for conventional diagnostic scanning when not in surgical mode.
Product Specification
Contact Information
MAIL
FONAR Corporation
110 Marcus Drive
Melville, N.Y. 11747
USA
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'FONAR Corporation':    | | |
• View the NEWS results for 'FONAR Corporation' (87).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
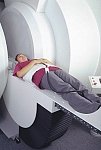
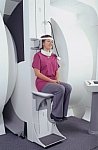
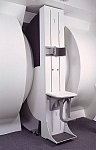
From FONAR Corporation;
in October of 2004, the company changed the product name of the Stand-Up™ MRI to the Upright™ MRI. The Indomitable™, Upright™ MRI is the only open MRI in the world that can perform positional MRI (pMRI), i.e. the Upright MRI™ scans patients in upright, weight-bearing positions, in addition to the conventional lie-down positions. The Upright™ MRI is the only device that can scan patients in the position their symptoms occur, in their position of pain. In early clinical reports independently confirm the effectiveness and potential of positional MRI. In October 2000, Fonar received permission to market the Indomitable™ from the FDA.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body -
weight-bearing MRI -
position imaging (flexion, extension, bending, standing, sitting and recumbent scanning)
CONFIGURATION Front-open and Top-open MRIPOWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Water, closed-loop | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Upright™ MRI' (5).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Upright™ MRI' (9).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Electromagnet' (24).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Electromagnet' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Upright MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) of the spine is a noninvasive procedure to evaluate different types of tissue, including the spinal cord, vertebral disks and spaces between the vertebrae through which the nerves travel, as well as distinguish healthy tissue from diseased tissue.
The cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine MRI should be scanned in individual sections.
The scan protocol parameter like e.g. the field of view ( FOV), slice thickness and matrix are usually different for cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine MRI, but the method
is similar. The standard views in the basic spinal MRI scan to create detailed slices (cross sections) are sagittal T1 weighted and T2 weighted images over the whole body part, and transverse (e.g. multi angle oblique) over the region of interest with different pulse sequences according to the result of the sagittal slices. Additional views or different types of pulse sequences like fat suppression, fluid attenuation inversion recovery ( FLAIR) or
diffusion weighted imaging are created dependent on the indication.
Indications:
•
Neurological deficit, evidence of radiculopathy, cauda equina compression
•
Primary tumors or drop metastases
•
Infection/inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis
•
Postoperative evaluation of lumbar spine: disk vs. scar
•
Localized back pain with no radiculopathy (leg pain)
Contrast enhanced MRI techniques delineate infections vs. malignancies, show a syrinx cavity and support to differentiate the postoperative conditions. After surgery for disk disease, significant fibrosis can occur in the spine. This scarring can mimic residual disk herniation. Magnetic resonance myelography evaluates spinal stenosis and various intervertebral discs can be imaged with multi angle oblique techniques. Cine series can be used to show true range of motion studies of parts of the spine.
Advanced open MRI devices are developed to perform positional scans in the position of pain or symptom (e.g. Upright™ MRI formerly Stand-Up MRI). | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Spine MRI' (11).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Spine MRI' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Hardware' (19).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Hardware' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 6) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |