 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |  | GRASE  GRAdient and Spin Echo GRAdient and Spin Echo | | | Searchterm 'grase' was found in the Abbreviation Register. | |
|  |
Result : Searchterm 'grase' found in 0 term [ ] and 4 definitions [ ] and 4 definitions [ ] ]
| 1 - 4 (of 4) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |  | | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Gradient and Spin Echo':    | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
Standard: head, body, C1, C3; Optional: Small joint, flex-E, flex-R, endocavitary (L and S), dual TMJ, knee, neck, T/L spine, breast; Optional phased array: Spine, pediatric, 3rd party connector, Flex-S-M-L, flex body, flex cardiac, neuro-vascular, head
SE, Modified-SE ( TSE), DAVE, STIR, FLAIR, SPIR, MTC, Dynamic, Keyhole, CLEAR, Q Flow, Balanced FFE, Multi Chunk 3D, Multi Stack 3D, FFE-EPI, SE-EPI, IR-EPI, GRASE, Diffusion Imaging, Perfusion Imaging;; Angiography: Inflow MRA, TONE, PCA, CE MRA
RapidView Recon. greater than 500 @ 256 Matrix
128 x 128, 256 x 256,512 x 512,1024 x 1024
Variable in 1% increments
Lum.: 120 cd/m2; contrast: 150:1
Variable (op. param. depend.)
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380/400 V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Intera 0.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
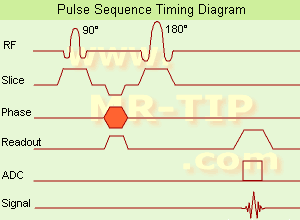
(SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. It uses 90° radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180° pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE).
In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the simplest form of a spin echo sequence is illustrated.
The 90° excitation pulse rotates the longitudinal magnetization ( Mz) into the xy-plane and the dephasing of the transverse magnetization (Mxy) starts.
The following application of a 180° refocusing pulse (rotates the magnetization in the x-plane) generates signal echoes. The purpose of the 180° pulse is to rephase the spins, causing them to regain coherence and thereby to recover transverse magnetization, producing a spin echo.
The recovery of the z-magnetization occurs with the T1 relaxation time and typically at a much slower rate than the T2-decay, because in general T1 is greater than T2 for living tissues and is in the range of 100-2000 ms.
The SE pulse sequence was devised in the early days of NMR days by Carr and Purcell and exists now in many forms: the multi echo pulse sequence using single or multislice acquisition, the fast spin echo (FSE/TSE) pulse sequence, echo planar imaging (EPI) pulse sequence and the gradient and spin echo ( GRASE) pulse sequence;; all are basically spin echo sequences.
In the simplest form of SE imaging, the pulse sequence has to be repeated as many times as the image has lines. Contrast values:
PD weighted: Short TE (20 ms) and long TR.
T1 weighted: Short TE (10-20 ms) and short TR (300-600 ms)
T2 weighted: Long TE (greater than 60 ms) and long TR (greater than 1600 ms)
With spin echo imaging no T2* occurs, caused by the 180° refocusing pulse. For this reason, spin echo sequences are more robust against e.g., susceptibility artifacts than gradient echo sequences.
See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram to find a description of the components.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Spin Echo Sequence' (24).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  | |  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 4 (of 4) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |