 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'table weight limit' found in 0 term [ ] and 0 definition [ ] and 0 definition [ ], (+ 5 Boolean[ ], (+ 5 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 5) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |  | | |  |  |  |
| |
|
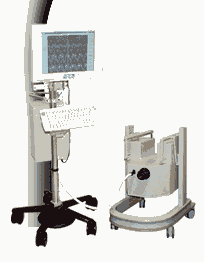
From MagneVu;
The MagneVu 1000 is a compact, robust, and por table, permanent magnet MRI system and operates without special shielding or costly site preparation.
This MRI device utilizes a patented non-homogeneous magnetic field image acquisition method to achieve high performance imaging. The MagneVu 1000 MRI scanner is designed for MRI of the extremities with the current specialty areas in diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Easy access is afforded for claustrophobic, pediatric, or limited mobility patients. In August 1998
FDA marketing clearance and other regulatory approvals have been received. Until 2008, over 130 devices in the US are in use. Some further developments of MagneVu's extremity scanner are: 'truly Plug n' Play MRI™' and iSiS ( which adds wireless capability to the second generation MV1000-XL).
Device Information and Specification IMAGING MODES 3-dimensional multi-echo data acquisition | |  | | | | • Share the entry 'MagneVu 1000':    | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
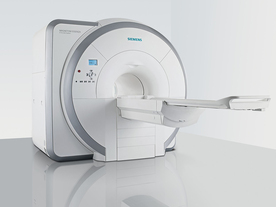
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2007.
The MAGNETOM Essenza is designed to combine high system performance with simple installation and power requirements to provide optimal operating costs for limited budgets. The standard system has up to 25 integrated coil elements and 8 independent radio frequency channels. Tim allows the combination of up to 4 different coils that reduce patient and coil repositioning.
The 1.5 Tesla system is designated for a complete range of clinical applications, including neurology, orthopedics, body imaging, angiography, cardiology, breast imaging, oncology and pediatric MRI.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra-short bore
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck, and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle, TMJ optional.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
8, 16
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
4350 kg in operation
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
145 x 226 x 216 cm
COOLING SYSTEM
Water; single cryogen, 2 stage refrigeration
30 mT/m, 300 msec to 10 mT/m
Passive, active; first order standard
second order optional
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 45 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
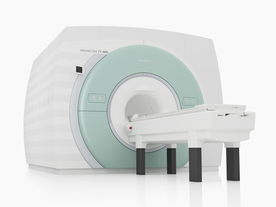
From Siemens Medical Systems;
The MAGNETOM 7T is designed as an open research platform. 7T MRI provides anatomical detail at the submil limiter scale, enhanced contrast mechanisms, outstanding spectroscopy performance, ultra-high resolution functional imaging ( fMRI), multinuclear whole-body MRI and functional information.
This ultra high field (UHF) MRI device is a research system and not cleared, approved or licensed in any jurisdiction for patient examinations.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
High-performance, ultra high field coils available. Integration and support for coil developments.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
32, optional 8 channels TX array
40 x 40 x 30 cm³ less than 8% nonlinearity
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
35017 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
320 x 240 x 317,5 cm
MAX. AMPLITUDE
up to 70 mT/m
Up to 3rd order shim coils, user configurable B0 shim ? B0 maps and ROI definition
POWER REQUIREMENTS
2000 Volts, 650A
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Categories of negative oral contrast agents:
Negative oral contrast media are usually based on superparamagnetic particles and act by inducing local field inhomogeneities, which results in shortening of both T1 and T2 relaxation times. Superparamagnetic contrast agents have predominant T2 weighted effects.
Biphasic contrast media are agents that have different signal intensities on different sequences, depending on the concentration at which they are used.
Sui table materials for oral contrast agents should have little or no absorption by the stomach or intestines, complete excretion, no motion or susceptibility artifacts, affordability, and uniform marking of the gastrointestinal tract.
Benefits of negative oral contrast agents are the reduction of ghosting artifacts caused by the lack of signal. Superparamagnetic iron oxides produce also in low concentrations a noticeable signal loss; but can generate susceptibility artifacts especially in gradient echo sequences. Perfluorochemicals do not dilute in the bowel because they are not miscible with water.
High cost, poor availability, and limited evaluations of side effects are possible disadvantages.
Negative oral contrast agents are used e.g., in MRCP, where the ingestion of 600-900 ml of SPIO cancels out the signal intensity of the lumen (in addition after the injection of a gadolinium-based contrast medium, the enhancement of the inflammatory tissues is clearer seen), and in MR abdominal imaging of Crohn's disease in combination with mannitol.

| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Negative Oral Contrast Agents' (7).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Open MRI scanners have been developed for people who are anxious or obese or for examination of small parts of the body, such as the extremities ( knee, shoulder). In addition, some systems offer imaging in different positions and sequences of movements.
The basic technology of an open MRI machine is similar to that of a traditional MRI device.
The major difference for the patient is that instead of lying in a narrow tunnel, the imaging table has more space around the body so that the magnet does not completely surround the person being tested.
Types of constructions:
•
Semi open high field MRI scanners provide an ultra short bore (tunnel) and widely flared ends. In this type of MRI systems, patients lie with the head in the space outside the bore, if for example the hips are examined.
•
Open low field MRI machines have often a wide open design, e.g. an open C-arm scanner is shaped like two large discs separated by a large pillar. Patients have an open sided feeling and more space around them allows a wider range of positions.
•
Advanced open MRI scanners combine the advantages of both, the high field strength, newest gradient technology and wide open design. Even scans of patients in upright, weight-bearing positions are possible (e.g. Upright™ MRI formerly Stand-Up MRI).
Difficulties with a traditional MRI scan include claustrophobia and patient size or, for health related reasons, patients who are not able to receive this type of diagnostic test. The MRI unit is a limited space, and some patients may be too large to fit in a narrow tunnel. In addition, weight limits can restrict the use of some scanners. The open MRI magnet has become the best option for those patients.
All of the highest resolution MRI scanners are tunnels and tend to accentuate the claustrophobic reaction. While patients may find the open MRI scanners easier to tolerate, some machines use a lower field magnet and generates lower image quality or have longer scan time. The better performance of an advanced open MRI scanner allows good image quality caused by the higher signal to noise ratio with maximum patient comfort.
See also Claustrophobia, MRI scan and Knee MRI. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Open MRI' (37).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Open MRI' (16).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 5) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |