 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  |
|  |  |
 |
| |
| | |  | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Induction' (1).
| | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Induction' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| | |  |
 |
| |
| | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Inferior' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| | |  | |  |  |
 |
| |
| From Philips Medical Systems;
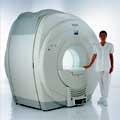
Philips Infinion 1.5 T is designed to maximize the efficiency and quality of patient care. Developed with the patient in mind, the Infinion is the shortest and most open 1.5T scanner available. The unique 'ultra short' 1.4 m magnet assures patient comfort and acceptance without compromising image quality and clinical performance.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra short bore
Head, head / neck, integrated C-spine, L/T spine array, small large GP coils, body flex array, torso pelvis array, breast array, endocavitary, shoulder array, lower extremity, hand / wrist, cardiac, PV array
SE, TSE, SS TSE, EPI, IR, STIR, FLAIR, FFE, TFE, T1 TFE, T2 TFE, Presat, Fatsat, MTC, Diff-opt., Angiography: PCA, MCA, TOF
IMAGING MODES
Single slice, single volume, multi slice, multi volume
80 images/sec std.; up to320 opt.@256
H*W*D
233 (lead fitted) x 198 x 140 cm
POWER REQUIREMENTS
400/480 V
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE
Closed loop, chilled water
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Infinion 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | | |  | |  |
 |
| |
| Inhomogeneity is the degree of lack of homogeneity, for example the fractional deviation of the local magnetic field from the average value of the field. Inhomogeneities of the static magnetic field, produced by the scanner as well as by object susceptibility, is unavoidable in MRI. The large value of gyromagnetic coefficient causes a significant frequency shift even for few parts per million field inhomogeneity, which in turn causes distortions in both geometry and intensity of the MR images.
Manufacturers try to make the magnetic field as homogeneous as possible, especially at the core of the scanner. Even with an ideal magnet, a little inhomogeneity is always left and is caused in addition by the susceptibility of the imaging object.
The geometrical distortion (displacement of the pixel locations) are important e.g., for some cases as stereotactic surgery. Displacements up to 3 to 5 mm have been reported. The second problem is the undesired changes in the intensity or brightness of pixels, which may cause problems in determining different tissues and reduce the maximum achievable image resolution.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Inhomogeneity' (21).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| | |  | |  |  |
| | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |