 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Amplitude' found in 1 term [ ] and 53 definitions [ ] and 53 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 31 - 35 (of 54) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Amplitude' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
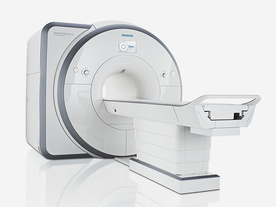
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2012.
The MAGNETOM Spectra is a cost-optimized high field MRI system with Tim 4G and Dot technologies. The system consumes less energy compared to other 3 Tesla scanners. The magnet-cooling helium is contained in a closed loop, which prevents the gas from escaping and reduces the need for refills. TimTX includes innovative techniques in the radio frequency excitation hardware as well as new application and processing features enabling uniform RF distribution in all body regions.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, neck and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle, endorectal optional.
Chemical shift imaging, single voxel spectroscopy
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
173 x 231 x 219 cm
COOLING SYSTEM
Water; single cryogen, 2 stage refrigeration
Passive, active; first order standard, second order optional
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; connection value with chiller 100 kvA /without chiller 60 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Amplitude' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
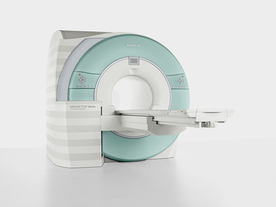
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2007.
The MAGNETOM Verio provides up to 102 integrated matrix coil elements and up to 32 independent radiofrequency channels that allow flexible coil combinations to make patient and coil repositioning virtually unnecessary. The Tim (total imaging matrix) technology also increases patient throughput due to a shorter scan time.
The open bore design offers great comfort for patients of all shapes and sizes.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra-short open bore
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle, TMJ optional.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
8, 18, 32
Chemical shift imaging, single voxel spectroscopy
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
8200 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
173 x 230 x 222 cm
Passive, active; first order,
second order standard
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 110 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
DESCRIPTION
Striped ghosts with a shift of half the field of view
Machine imperfection-based artifacts manifest themselves due to the fact that the odd k-space lines are acquired in a different direction than the even k-space lines. Slight differences in timing result in shifts of the echo in the acquisition window. By the shift theorem, such shifts in the time domain data then produce linear phase differences in the frequency domain data.
Without correction, such phase differences in every second line produce striped ghosts with a shift of half the field of view, so-called Nyquist ghosts. Shifts in the applied magnetic field can also produce similar (but constant in amplitude) ghosts.
This artifact is commonly seen in an EPI image and can arise from both, hardware and sample imperfections.
A further source of machine-based artifact arises from the need to acquire the signal as quickly as possible. For this reason the EPI signal is often acquired during times when the gradients are being switched. Such sampling effectively means that the k-space sampling is not uniform, resulting in ringing artifacts in the image.

Image Guidance
Such artifacts can be minimized by careful setup of the spectrometer and/or correction of the data. For this reasons reference data are often collected, either as a separate scan or embedded in the imaging data.
The non-uniform sampling can be removed by knowing the form of the gradient switching. It is possible to regrid the data onto a uniform k-space grid. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Machine Imperfection Artifact' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Amplitude' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  | |  |  | Searchterm 'Amplitude' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
NAME
Motion, phase encoded motion, instability, smearing
REASON
Movement of the imaged object
HELP
Compensation techniques, more averages, anti spasmodic
Patient motion is the largest physiological effect that causes artifacts, often resulting from involuntary movements (e.g. respiration, cardiac motion and blood flow, eye movements and swallowing) and minor subject movements.
Movement of the object being imaged during the sequence results in inconsistencies in phase and amplitude, which lead to blurring and ghosting. The nature of the artifact depends on the timing of the motion with respect to the acquisition. Causes of motion artifacts can also be mechanical vibrations, cryogen boiling, large iron objects moving in the fringe field (e.g. an elevator), loose connections anywhere, pulse timing variations, as well as sample motion. These artifacts appear in the phase encoding direction, independent of the direction of the motion.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Motion Artifact' (24).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |