 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Body Coil' found in 1 term [ ] and 31 definitions [ ] and 31 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 16 - 20 (of 32) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7] [2 3 4 5 6 7] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Body Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
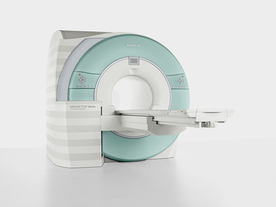
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2007.
The MAGNETOM Verio provides up to 102 integrated matrix coil elements and up to 32 independent radiofrequency channels that allow flexible coil combinations to make patient and coil repositioning virtually unnecessary. The Tim (total imaging matrix) technology also increases patient throughput due to a shorter scan time.
The open bore design offers great comfort for patients of all shapes and sizes.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra-short open bore
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle, TMJ optional.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
8, 18, 32
Chemical shift imaging, single voxel spectroscopy
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
8200 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
173 x 230 x 222 cm
Passive, active; first order,
second order standard
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 110 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
From Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc.; because of its dependability, the MRP-7000™ remains popular more than a decade after the first U.S. system was shipped. This system maintains a high resale value, what has made it one of the most sought-after scanners on the used MRI equipment market.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body DualQuad T/R Body Coil, MA Head, MA C-Spine, MA Shoulder, MA Wrist, MA CTL Spine, MA Knee, MA TMJ, MA Flex Body (3 sizes), Neck, small and large Extremity, PVA (WIP), Breast (WIP), Neurovascular (WIP), Cardiac (WIP) and MA Foot//Ankle (WIP) SE, GE, GR, IR, FIR, STIR, ss-FSE, FSE, DE-FSE/FIR, FLAIR, ss/ms-EPI, ss/ms EPI- DWI, SSP, MTC, SE/GE-EPI, MRCP, SARGE, RSSG, TRSG, BASG, Angiography: CE, PC, 2D/3D TOFIMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study horizontal 2.5 m x 2.1 m vertical | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRP-7000™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Phased Array Coil' (9).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Body Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Sense Coil' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(SENSE) A MRI technique for relevant scan time reduction. The spatial information related to the coils of a receiver array are utilized for reducing conventional Fourier encoding. In principle, SENSE can be applied to any imaging sequence and k-space trajectories. However, it is particularly feasible for Cartesian sampling schemes. In 2D Fourier imaging with common Cartesian sampling of k-space sensitivity encoding by means of a receiver array enables to reduce the number of Fourier encoding steps.
SENSE reconstruction without artifacts relies on accurate knowledge of the individual coil sensitivities. For sensitivity assessment, low-resolution, fully Fourier-encoded reference images are required, obtained with each array element and with a body coil.
The major negative point of parallel imaging techniques is that they diminish SNR in proportion to the numbers of reduction factors.
R is the factor by which the number of k-space samples is reduced. In standard Fourier imaging reducing the sampling density results in the reduction of the FOV, causing aliasing. In fact, SENSE reconstruction in the Cartesian case is efficiently performed by first creating one such aliased image for each array element using discrete Fourier transformation (DFT).
The next step then is to create a full-FOV image from the set of intermediate images. To achieve this one must undo the signal superposition underlying the fold-over effect. That is, for each pixel in the reduced FOV the signal contributions from a number of positions in the full FOV need to be separated. These positions form a Cartesian grid corresponding to the size of the reduced FOV.
The advantages are especially true for contrast-enhanced MR imaging such as
dynamic liver MRI (liver imaging) ,
3 dimensional magnetic resonance angiography (3D MRA), and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreaticography ( MRCP).
The excellent scan speed of SENSE allows for acquisition of two separate sets of hepatic MR images within the time regarded as the hepatic arterial-phase (double arterial-phase technique) as well as that of multidetector CT.
SENSE can also increase the time efficiency of spatial signal encoding in 3D MRA. With SENSE, even ultrafast (sub second) 4D MRA can be realized.
For MRCP acquisition, high-resolution 3D MRCP images can be constantly provided by SENSE. This is because SENSE resolves the presence of the severe motion artifacts due to longer acquisition time. Longer acquisition time, which results in diminishing image quality, is the greatest problem for 3D MRCP imaging.
In addition, SENSE reduces the train of gradient echoes in combination with a faster k-space traversal per unit time, thereby dramatically improving the image quality of single shot echo planar imaging (i.e. T2 weighted, diffusion weighted imaging). | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Sensitivity Encoding' (12).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |