 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Data Acquisition Time' found in 1 term [ ] and 2 definitions [ ] and 2 definitions [ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 22) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Data Acquisition Time' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
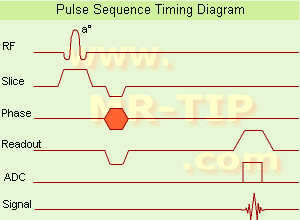
(GRE - sequence) A gradient echo is generated by using a pair of bipolar gradient pulses. In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the basic gradient echo sequence is illustrated. There is no refocusing 180° pulse and the data are sampled during a gradient echo, which is achieved by dephasing the spins with a negatively pulsed gradient before they are rephased by an opposite gradient with opposite polarity to generate the echo.
See also the Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram. There you will find a description of the components.
The excitation pulse is termed the alpha pulse α. It tilts the magnetization by a flip angle α, which is typically between 0° and 90°. With a small flip angle there is a reduction in the value of transverse magnetization that will affect subsequent RF pulses.
The flip angle can also be slowly increased during data acquisition (variable flip angle: tilt optimized nonsaturation excitation).
The data are not acquired in a steady state, where z-magnetization recovery and destruction by ad-pulses are balanced.
However, the z-magnetization is used up by tilting a little more of the remaining z-magnetization into the xy-plane for each acquired imaging line.
Gradient echo imaging is typically accomplished by examining the FID, whereas the read gradient is turned on for localization of the signal in the readout direction. T2* is the characteristic decay time constant associated with the FID. The contrast and signal generated by a gradient echo depend on the size of the longitudinal magnetization and the flip angle.
When α = 90° the sequence is identical to the so-called partial saturation or saturation recovery pulse sequence.
In standard GRE imaging, this basic pulse sequence is repeated as many times as image lines have to be acquired.
Additional gradients or radio frequency pulses are introduced with the aim to spoil to refocus the xy-magnetization at the moment when the spin system is subject to the next α pulse.
As a result of the short repetition time, the z-magnetization cannot fully recover and after a few initial α pulses there is an equilibrium established between z-magnetization recovery and z-magnetization reduction due to the α pulses.
Gradient echoes have a lower SAR, are more sensitive to field inhomogeneities and have a reduced crosstalk, so that a small or no slice gap can be used.
In or out of phase imaging depending on the selected TE (and field strength of the magnet) is possible.
As the flip angle is decreased, T1 weighting can be maintained by reducing the TR.
T2* weighting can be minimized by keeping the TE as short as possible, but pure T2 weighting is not possible.
By using a reduced flip angle, some of the magnetization value remains longitudinal (less time needed to achieve full recovery) and for a certain T1 and TR, there exist one flip angle that will give the most signal, known as the "Ernst angle".
Contrast values:
PD weighted: Small flip angle (no T1), long TR (no T1) and short TE (no T2*)
T1 weighted: Large flip angle (70°), short TR (less than 50ms) and short TE
T2* weighted: Small flip angle, some longer TR (100 ms) and long TE (20 ms)
Classification of GRE sequences can be made into four categories:
See also Gradient Recalled Echo Sequence, Spoiled Gradient Echo Sequence, Refocused Gradient Echo Sequence, Ultrafast Gradient Echo Sequence.
| | | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Contrast enhanced MRI is a commonly used procedure in magnetic resonance imaging. The need to more accurately characterize different types of lesions and to detect all malignant lesions is the main reason for the use of intravenous contrast agents.
Some methods are available to improve the contrast of different tissues. The focus of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) is on contrast kinetics with demands for spatial resolution dependent on the application. DCE- MR imaging is used for diagnosis of cancer (see also liver imaging, abdominal imaging, breast MRI, dynamic scanning) as well as for diagnosis of cardiac infarction (see perfusion imaging, cardiac MRI). Quantitative DCE-MRI requires special data acquisition techniques and analysis software.
Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) allows the visualization of vessels and the temporal resolution provides a separation of arteries and veins. These methods share the need for acquisition methods with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Double contrast administration (combined contrast enhanced (CCE) MRI) uses two contrast agents with complementary mechanisms e.g., superparamagnetic iron oxide to darken the background liver and gadolinium to brighten the vessels. A variety of different categories of contrast agents are currently available for clinical use.
Reasons for the use of contrast agents in MRI scans are:
•
Relaxation characteristics of normal and pathologic tissues are not always different enough to produce obvious differences in signal intensity.
•
Pathology that is some times occult on unenhanced images becomes obvious in the presence of contrast.
•
Enhancement significantly increases MRI sensitivity.
•
In addition to improving delineation between normal and abnormal tissues, the pattern of contrast enhancement can improve diagnostic specificity by facilitating characterization of the lesion(s) in question.
•
Contrast can yield physiologic and functional information in addition to lesion delineation.
Common Indications:
Brain MRI : Preoperative/pretreatment evaluation and postoperative evaluation of brain tumor therapy, CNS infections, noninfectious inflammatory disease and meningeal disease.
Spine MRI : Infection/inflammatory disease, primary tumors, drop metastases, initial evaluation of syrinx, postoperative evaluation of the lumbar spine: disk vs. scar.
Breast MRI : Detection of breast cancer in case of dense breasts, implants, malignant lymph nodes, or scarring after treatment for breast cancer, diagnosis of a suspicious breast lesion in order to avoid biopsy.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com.
See also Blood Pool Agents, Myocardial Late Enhancement, Cardiovascular Imaging, Contrast Enhanced MR Venography, Contrast Resolution, Dynamic Scanning, Lung Imaging, Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents, Contrast Medium and MRI Guided Biopsy. | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast Enhanced MRI' (14).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Enhanced MRI' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
FDA Approves Gadopiclenol for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.pharmacytimes.com |  |  |
Effect of gadolinium-based contrast agent on breast diffusion-tensor imaging
Thursday, 6 August 2020 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Artificial Intelligence Processes Provide Solutions to Gadolinium Retention Concerns
Thursday, 30 January 2020 by www.itnonline.com |  |  |
Accuracy of Unenhanced MRI in the Detection of New Brain Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis
Tuesday, 12 March 2019 by pubs.rsna.org |  |  |
The Effects of Breathing Motion on DCE-MRI Images: Phantom Studies Simulating Respiratory Motion to Compare CAIPIRINHA-VIBE, Radial-VIBE, and Conventional VIBE
Tuesday, 7 February 2017 by www.kjronline.org |  |  |
Novel Imaging Technique Improves Prostate Cancer Detection
Tuesday, 6 January 2015 by health.ucsd.edu |  |  |
New oxygen-enhanced MRI scan 'helps identify most dangerous tumours'
Thursday, 10 December 2015 by www.dailymail.co.uk |  |  |
All-organic MRI Contrast Agent Tested In Mice
Monday, 24 September 2012 by cen.acs.org |  |  |
A groundbreaking new graphene-based MRI contrast agent
Friday, 8 June 2012 by www.nanowerk.com |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
In parallel MR imaging, a reduced data set in the phase encoding direction(s) of k-space is acquired to shorten acquisition time, combining the signal of several coil arrays. The spatial information related to the phased array coil elements is utilized for reducing the amount of conventional Fourier encoding.
First, low-resolution, fully Fourier-encoded reference images are required for sensitivity assessment. Parallel imaging reconstruction in the Cartesian case is efficiently performed by creating one aliased image for each array element using discrete Fourier transformation. The next step then is to create an full FOV image from the set of intermediate images.
Parallel reconstruction techniques can be used to improve the image quality with increased signal to noise ratio, spatial resolution, reduced artifacts, and the temporal resolution in dynamic MRI scans.
Parallel imaging algorithms can be divided into 2 main groups:
Image reconstruction produced by each coil ( reconstruction in the image domain, after Fourier transform): SENSE ( Sensitivity Encoding), PILS (Partially Parallel Imaging with Localized Sensitivity),
ASSET.
Reconstruction of the Fourier plane of images from the frequency signals of each coil ( reconstruction in the frequency domain, before Fourier transform): GRAPPA. Additional techniques include SMASH, SPEEDER™,
IPAT (Integrated Parallel Acquisition Techniques - derived of GRAPPA a k-space based technique) and mSENSE (an image based enhanced version of SENSE).
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Parallel Imaging Technique' (12).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Data Acquisition Time' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(BW) Bandwidth is a measure of frequency range, the range between the highest and lowest frequency allowed in the signal. For analog signals, which can be mathematically viewed as a function of time, bandwidth is the width, measured in Hertz of a frequency range in which the signal's Fourier transform is nonzero.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Bandwidth' (19).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(CE MRA) Contrast enhanced MR angiography is based on the T1 values of blood, the surrounding tissue, and paramagnetic contrast agent.
T1-shortening contrast agents reduces the T1 value of the blood (approximately to 50 msec, shorter than that of the surrounding tissues) and allow the visualization of blood vessels, as the images are no longer dependent primarily on the inflow effect of the blood.
Contrast enhanced MRA is performed with a short TR to have low signal (due to the longer T1) from the stationary tissue, short scan time to facilitate breath hold imaging, short TE to minimize T2* effects and a bolus injection of a sufficient dose of a gadolinium chelate.
Images of the region of interest are performed with 3D spoiled gradient echo pulse sequences. The enhancement is maximized by timing the contrast agent injection such that the period of maximum arterial concentration corresponds to the k-space acquisition. Different techniques are used to ensure optimal contrast of the arteries e.g., bolus timing, automatic bolus detection, bolus tracking, care bolus.
A high resolution with near isotropic voxels and minimal pulsatility and misregistration artifacts should be striven for. The postprocessing with the maximum intensity projection ( MIP) enables different views of the 3D data set.
Unlike conventional MRA techniques based on velocity dependent inflow or phase shift techniques, contrast enhanced MRA exploits the
gadolinium induced T1-shortening effects. CE MRA reduces or eliminates most of the artifacts of time of flight angiography or phase contrast angiography. Advantages are the possibility of in plane imaging of the blood vessels, which allows to examine large parts in a short time and high resolution scans in one breath hold.
CE MRA has found a wide acceptance in the clinical routine, caused by the
advantages:
•
3D MRA can be acquired in any plane, which means that
greater vessel coverage can be obtained at high
resolution with fewer slices (aorta, peripheral vessels);
•
the possibility to perform a time resolved examination
(similarly to conventional angiography);
•
no use of ionizing radiation; paramagnetic agents have a beneficial safety.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography' (14).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Angiography' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |