 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Dynamic Range' found in 1 term [ ] and 6 definitions [ ] and 6 definitions [ ], (+ 3 Boolean[ ], (+ 3 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 10) Result Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Dynamic Range' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|

From GE Healthcare;
The Signa SP 0.5T™ is an open MRI magnet that is designed for use in interventional radiology and intra-operative imaging. The vertical gap configuration increases patient positioning options, improves patient observation, and allows continuous access to the patient during imaging.
The magnet enclosure also incorporates an intercom, patient observation video camera, laser patient alignment lights, and task lighting in the imaging volume.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Integrated transmit and receive body coil; optional rotational body coil, head; other coils optional; open architecture makes system compatible with a wide selection of coilsarray Standard: SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE and SPGR, 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D FSE, 2D/3D FGRE and FSPGR, SSFP, FLAIR, EPI, optional: 2D/3D Fiesta, true chem sat, fat/water separation, single shot diffusion EPI IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF TR 1.3 to 12000 msec in increments of 1 msec TE 0.4 to 2000 msec in increments of 1 msec 2D: 1.4mm - 20mm 3D: 0.2mm - 20mm POWER REQUIREMENTS 200 - 480, 3-phase | |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Dynamic Range' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
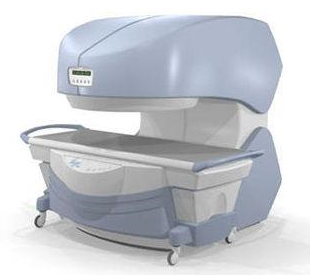
From
Millennium Technology Inc.
This open C-shaped MRI system eases patient comfort and technologist maneuverability. This low cost scanner is build for a wide range of applications. The Virgo™ patient table is detachable and moves on easy rolling castors. Able to accommodate patient weights up to 160 kg, the tabletop has a range of motion of 30 cm in the lateral direction and 90cm in the longitudinal direction. Images generated with this scanner can only be viewed (without data loss) on Millennium's proprietary viewing software.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head, Body, Neck, Knee, Shoulder,
Spine, Wrist, Breast, Extremity, Lumbar Spine, TMJ
IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
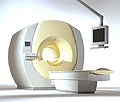
From Philips Medical Systems;
the Intera-family offers with this member a wide range of possibilities, efficiency and a ergonomic and intuitive serving-platform. Also available as Intera CV for cardiac and Intera I/T for interventional MR procedures.
The scanners are also equipped with SENSE technology, which is essential for high-quality contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography, interactive cardiac MR and diffusion tensor imaging ( DTI) fiber tracking.
The increased accuracy and clarity of MR scans obtained with this technology allow for faster and more accurate diagnosis of potential problems like patient friendliness and expands the breadth of applications including cardiology, oncology and interventional MR.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
Standard: head, body, C1, C3; Optional: Small joint, flex-E, flex-R, endocavitary (L and S), dual TMJ, knee, neck, T/L spine, breast; Optional phased array: Spine, pediatric, 3rd party connector; Optional SENSE coils: Flex-S-M-L, flex body, flex cardiac
SE, Modified-SE ( TSE), IR (T1, T2, PD), STIR, FLAIR, SPIR, FFE, T1-FFE, T2-FFE, Balanced FFE, TFE, Balanced TFE, Dynamic, Keyhole, 3D, Multi Chunk 3D, Multi Stack 3D, K Space Shutter, MTC, TSE, Dual IR, DRIVE, EPI, Cine, 2DMSS, DAVE, Mixed Mode; Angiography: PCA, MCA, Inflow MRA, CE
TR
2.9 (Omni), 1.6 (Power), 1.6 (Master/Expl) msec
TE
1.0 (Omni), 0.7 (Power), 0.5 (Master/Expl) msec
RapidView Recon. greater than 500 @ 256 Matrix
0.1 mm(Omni), 0.05 mm (Pwr/Mstr/Expl)
128 x 128, 256 x 256,512 x 512,1024 x 1024 (64 for BOLD img.)
Variable in 1% increments
Lum.: 120 cd/m2; contrast: 150:1
Variable (op. param. depend.)
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380/400 V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Intera 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Dynamic Range' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
A series of rapidly recorded multiple images taken at sequential cycles of time and displayed on a monitor in a dynamic movie display format. This technique can be used to show true range of motion studies of joints and parts of the spine. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Cine' (57).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Cine' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Dynamic Range' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Liver imaging can be performed with sonography, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI). Ultrasound is, caused by the easy access, still the first-line imaging method of choice; CT and MRI are applied whenever ultrasound imaging yields vague results. Indications are the characterization of metastases and primary liver tumors e.g., benign lesions such as focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH), adenoma, hemangioma and malignant lesions (cancer) such as hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC).
The decision, which medical imaging modality is more suitable, MRI or CT, is dependent on the different factors. CT is less costly and more widely available; modern multislice scanners provide high spatial resolution and short scan times but has the disadvantage of radiation exposure.
With the introduction of high performance MR systems and advanced sequences the image quality of MRI for the liver has gained substantially. Fast spin echo or single shot techniques, often combined with fat suppression, are the most common T2 weighted sequences used in liver MRI procedures.
Spoiled gradient echo sequences are used as ideal T1 weighted sequences for evaluating of the liver. The repetition time (TR) can be sufficiently long to acquire enough sections covering the entire liver in one pass, and to provide good signal to noise. The TE should be the shortest in phase echo time (TE), which provides strong T1 weighting, minimizes magnetic susceptibility effects, and permits acquisition within one breath hold to cover the whole liver. A flip angle of 80° provides good T1 weighting and less of power deposition and tissue saturation than a larger flip angle that would provide comparable T1 weighting.
Liver MRI is very dependent on the administration of contrast agents, especially when detection and characterization of focal lesions are the issues. Liver MRI combined with MRCP is useful to evaluate patients with hepatic and biliary disease.
Gadolinium chelates are typical non-specific extracellular agents diffusing rapidly to the extravascular space of tissues being cleared by glomerular filtration at the kidney. These characteristics are somewhat problematic when a large organ with a huge interstitial space like the liver is imaged. These agents provide a small temporal imaging window (seconds), after which they begin to diffuse to the interstitial space not only of healthy liver cells but also of lesions, reducing the contrast gradient necessary for easy lesion detection. Dynamic MRI with multiple phases after i.v. contrast media (Gd chelates), with arterial, portal and late phase images (similar to CT) provides additional information.
An additional advantage of MRI is the availability of liver-specific contrast agents (see also Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents). Gd-EOB-DTPA (gadoxetate disodium, Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl dimeglumine, EOVIST Injection, brand name in other countries is Primovist) is a gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent approved by the FDA for the detection and characterization of known or suspected focal liver lesions.
Gd-EOB-DTPA provides dynamic phases after intravenous injection, similarly to non-specific gadolinium chelates, and distributes into the hepatocytes and bile ducts during the hepatobiliary phase. It has up to 50% hepatobiliary excretion in the normal liver.
Since ferumoxides are not eliminated by the kidney, they possess long plasmatic half-lives, allowing circulation for several minutes in the vascular space. The uptake process is dependent on the total size of the particle being quicker for larger particles with a size of the range of 150 nm (called superparamagnetic iron oxide). The smaller ones, possessing a total particle size in the order of 30 nm, are called ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles and they suffer a slower uptake by RES cells. Intracellular contrast agents used in liver MRI are primarily targeted to the normal liver parenchyma and not to pathological cells. Currently, iron oxide based MRI contrast agents are not marketed.
Beyond contrast enhanced MRI, the detection of fatty liver disease and iron overload has clinical significance due to the potential for evolution into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Imaging-based liver fat quantification (see also Dixon) provides noninvasively information about fat metabolism; chemical shift imaging or T2*-weighted imaging allow the quantification of hepatic iron concentration.
See also Abdominal Imaging, Primovistâ„¢, Liver Acquisition with Volume Acquisition (LAVA), T1W High Resolution Isotropic Volume Examination (THRIVE) and Bolus Injection.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Liver Sonography at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com. | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Liver Imaging' (13).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Liver Imaging' (10).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Utility and impact of magnetic resonance elastography in the clinical course and management of chronic liver disease
Saturday, 20 January 2024 by www.nature.com |  |  |
Even early forms of liver disease affect heart health, Cedars-Sinai study finds
Thursday, 8 December 2022 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
For monitoring purposes, AI-aided MRI does what liver biopsy does with less risk, lower cost
Wednesday, 28 September 2022 by radiologybusiness.com |  |  |
Perspectum: High Liver Fat (Hepatic Steatosis) Linked to Increased Risk of Hospitalization in COVID-19 Patients With Obesity
Monday, 29 March 2021 by www.businesswire.com |  |  |
EMA's final opinion confirms restrictions on use of linear gadolinium agents in body scans
Friday, 21 July 2017 by www.ema.europa.eu |  |  |
T2-Weighted Liver MRI Using the MultiVane Technique at 3T: Comparison with Conventional T2-Weighted MRI
Friday, 16 October 2015 by www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
EORTC study aims to qualify ADC as predictive imaging biomarker in preoperative regimens
Monday, 4 January 2016 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
MRI effectively measures hemochromatosis iron burden
Saturday, 3 October 2015 by medicalxpress.com |  |  |
Total body iron balance: Liver MRI better than biopsy
Sunday, 15 March 2015 by www.eurekalert.org |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | previous 6 - 10 (of 10) Result Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |