 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Field Strength' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
MRI can be indicated for use in pregnant women if other forms of diagnostic imaging are inadequate or require exposure to ionizing radiation such as X-ray or CT.
As a safety precaution, MR scanning should be avoided in the first three months of pregnancy.
Similar considerations hold for pregnant staff of a magnetic resonance department. An epidemiological study (by Kanal, et al.) concluded that data collected from MRI technologists were negative with respect to any statistically significant elevations in the rates of spontaneous abortion, infertility and premature delivery.
However, also for psychological reasons, it might be a wise precaution that pregnant staff members do not remain in the scan room during actual scanning.
There have been several reports (results could not be reproduced) that static magnetic fields may provoke genetic mutations, changes in growth rate and leukocyte count and other effects.
No reports have been published that persons exposed to magnetic fields, including staff at MR departments, have a higher incidence of genetic damage to their children than found in the average population.
This research needs further investigation and for this purpose pregnancy should be considered a relative contraindication for MR spectroscopy and MRI procedures.
Taking into account that clinical MR imaging devices operate at field strengths of between 0.2 and 2.0 T, higher field strengths need more investigation.

| | | |  | | • For this and other aspects of MRI safety see our InfoSheet about MRI Safety. | | | • Patient-related information is collected in our MRI Patient Information.
| | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Field Strength' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(SAR) The Specific Absorption Rate is defined as the RF power absorbed per unit of mass of an object, and is measured in watts per kilogram (W/kg).
The SAR describes the potential for heating of the patient's tissue due to the application of the RF energy necessary to produce the MR signal. Inhomogeneity of the RF field leads to a local exposure where most of the absorbed energy is applied to one body region rather than the entire person, leading to the concept of a local SAR. Hot spots may occur in the exposed tissue, to avoid or at least minimize effects of such theoretical complications, the frequency and the power of the radio frequency irradiation should be kept at the lowest possible level. Averaging over the whole body leads to the global SAR.
It increases with field strength, radio frequency power and duty cycle, transmitter-coil type and body size. The doubling of the field strength from 1.5 Tesla (1.5T) to 3 Tesla ( 3T) leads to a quadrupling of SAR. In high and ultrahigh fields, some of the multiple echo, multiple-slice pulse sequences may create a higher SAR than recommended by the agencies. SAR can be reduced by lower flip angle and longer repetition times, which could potentially affect image contrast.
Normally no threatening increase in temperature could be shown. Even in high magnetic fields, the local temperature increases not more than 1°C. 2.1°C is the highest measured increase in skin temperature. Eddy currents may heat up implants and thus may cause local heating.
FDA SAR limits:
•
Whole body: 4W/kg/15-minute exposure averaged;
•
Head: 3W/kg/10-minute exposure averaged;
•
Head or torso: 8W/kg/5 minute exposure per gram of tissue;
•
Extremities: 12W/kg/5 minute exposure per gram of tissue.
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) SAR limits of some European countries:
All limits are averaged over 6 minutes.
•
Level 0 (normal operating mode): Whole body 2W/kg; Head 3.2W/kg; Head or Torso (local) 10W/kg;
Extremities (local) 20W/kg;
•
Level I (first level controlled operating mode): Whole body 4W/kg; Head 3.2W/kg; Head or Torso (local) 10W/kg; Extremities (local) 20W/kg;
•
Level II (second level controlled operating mode): All values are over Level I values.
(For more details: IEC 60601-2-33 (2002))
In most countries standard MRI systems are limited to a maximum SAR of 4 W/kg, so most scanning in level II is impossible.
For Level I, in addition to routine monitoring, particular caution must be exercised for patients who are sensitive to temperature increases or to RF energy.
For Japan different SAR limits are valid. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Specific Absorption Rate' (8).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Specific Absorption Rate' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | MRI Safety Resources | | | | |
|  |  |  |
| |
|
Superconducting magnets are electromagnets that are partially built from
superconducting materials and therefore reach much higher magnetic field intensity.
The coil windings of superconducting magnets are made of wires of a type 2 superconductor (mostly used is niobium-titanium - up to 15 Tesla the critical temperature is less then 10 Kelvin). These coils have no resistance when operated at temperatures near absolute zero (-273.15°C, -459°F, 0 K).
Liquid helium (4.2 K) is commonly used as a coolant (sometimes in addition with a second cryogen liquid nitrogen as an intermediate thermal shield to reduce the boil-off rate of liquid helium), which consequently conclude refilling (intervals: liquid helium ~ 3 month, liquid nitrogen ~ 2 weeks). There are cryogen-free superconducting magnets with a closed-cycle refrigerating system at the horizon. Superconducting magnets typically exhibit field strengths of greater than 0.5 T, operate clinically up to 3 T, and have a horizontal field orientation, which makes them prone to missile effects without significant magnetic shielding.
See also Quenching.
See also the related poll result: ' In 2010 your scanner will probably work with a field strength of' | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Superconducting Magnet' (15).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Superconducting Magnet' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Field Strength' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
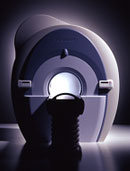
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
With its high- field strength, the Vantage™ delivers the clinical capabilities and image quality expected by cardiologists, while simultaneously offering patients a more comfortable and non-invasive option, said Dane Peshe, director, MRI Business Unit, Toshiba America Medical Systems. Vantage™ supports a full complement of cardiovascular imaging studies, ranging from stroke evaluation to peripheral vascular imaging. Additionally, the ultra short bore design offers patients a greater feeling of openness that reduces claustrophobic sensations, while Toshiba's exclusive, patented Pianissimo™ technology reduces scan noise by as much as 90 percent for a more pleasant experience.'
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body CONFIGURATION Ultra short bore SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, EPI, SuperFASE; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study 32-1024, phase;; 64-1024, freq. POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled Liquid helium: approx. less than 0.05 L/hr Passive, active, auto-active | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Vantage™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Field Strength' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
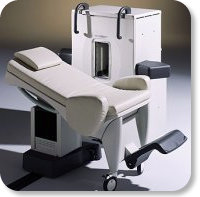
Developed by GE Lunar; the ARTOSCAN™-M is designed specifically for in-office musculoskeletal imaging. ARTOSCAN-M's compact, modular design allows placing within a clinical environment, bringing MRI to the patient. Patients remain outside the magnet at all times during the examinations, enabling constant patient-technologist contact. ARTOSCAN-M requires no special RF room, magnetic shielding, special power supply or air conditioning.
The C-SCAN™ (also known as Artoscan C) is developed from the ARTOSCAN™ - M, with a new computer platform.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Dedicated extremity
SE, GE, IR, STIR, FSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE
SLICE THICKNESS
2D: 2 mm - 10 mm;
3D: 0.6 mm - 10 mm
4,096 gray lvls, 256 lvls in 3D
POWER REQUIREMENTS
100/110/200/220/230/240V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'ARTOSCAN™ - M' (3).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |