 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Image Quality' found in 1 term [ ] and 44 definitions [ ] and 44 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 26 - 30 (of 45) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Image Quality' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
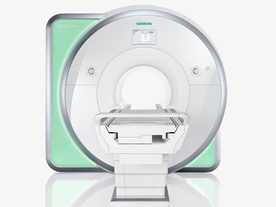
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2010.
The MAGNETOM Aera is a patient friendly, comfortable 1.5 Tesla MRI system with advanced radio frequency chain.
The system is equipped with the Tim 4G and Dot system (Total imaging matrix + Day optimizing throughput), to enhance both productivity and image quality.
Tim 4G technology provides improved SNR. The standard system configuration of 48 radio frequency channels and 204 coil elements creates an imaging matrix that allows maximum use of coil elements at full field of view. Dot provides improved image consistency through new features like auto align, auto FoV and automatic bolus detection.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder. Up to 60% more SNR with Tim 4G.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
48, 64
MINIMUM TE
3-D GRE: 0.22 (256 matrix), Ultra-short TE
At isocenter: L-R 70 cm, A-P (with table) 55 cm
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
3121 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
145 x 231 x 219 cm
MAX. AMPLITUDE
33 or 45 mT/m
3 linear with 20 coils, 5 nonlinear 2nd-order
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 85 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Image Quality' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
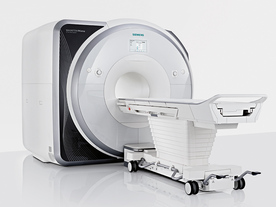
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2013.
The MAGNETOM Prisma is the 3T PowerPack for exploration that offers most demanding clinical and research challenges of today and the future. The latest parallel transmit technology, TimTX TrueShape, enables zooming into specific body regions for enhanced image quality. Furthermore, the Tim 4G integrated coil technology offers remarkable imaging flexibility and supports complex
examinations across the whole body.
Onsite upgrades to the MAGNETOM Prisma for customers who have already installed the 3 Tesla MAGNETOM Trio are possible.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
CONFIGURATION
Ultra-short bore
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
64, 128
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
13000 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
173 x 230 x 222 cm
Passive, active; first order,
second order
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground;
| |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
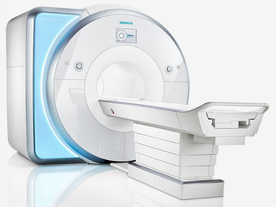
From Siemens Medical Systems;
Received FDA clearance in 2010.
MAGNETOM Skyra is a top-of-the-line, patient friendly wide bore 3 Tesla MRI system.
The system is equipped with the Tim 4G and Dot system (Total imaging matrix and Day optimizing throughput), to enhance both productivity and image quality with the complete range of advanced applications for clinical routine and research. Tim 4G features lighter, trimmer MRI coils that take up less space inside the magnet but deliver a high coil element density with increased signal to noise ratio and the possibility to use high iPAT factors.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole Body
Head, spine, torso/ body coil, neurovascular, cardiac, neck, shoulder, knee, wrist, foot//ankle and multi-purpose flex coils. Peripheral vascular, breast, shoulder.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
48, 64, 128
Chemical shift imaging, single voxel spectroscopy
MINIMUM TE
3D T1 spoiled GRE: 0.22 (256 matrix), Ultra-short TE
At isocenter: L-R 70 cm, A-P (with table) 55 cm
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
5768 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
173 x 231 x 219 cm
COOLING SYSTEM
Water; single cryogen, 2 stage refrigeration
3 linear with 20 coils, 5 nonlinear 2nd-order
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380 / 400 / 420 / 440 / 460 / 480 V, 3-phase + ground; 110 kVA
| |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Image Quality' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
The MRI device is located within a specially shielded room ( Faraday cage) to avoid outside interference, caused by the use of radio waves very close in frequency to those of ordinary FM radio stations.
The MRI procedure can easily be performed through clothing and bones, but attention must be paid to ferromagnetic items, because they will be attracted from the magnetic field. A hospital gown is appropriate, or the patient should wear clothing without metal fasteners and remove any metallic objects like hairpins, jewelry, eyeglasses, clocks, hearing aids, any removable dental work, lighters, coins etc., not only for MRI safety reasons.
Metal in or around the scanned area can also cause errors in the reconstructed images ( artifacts). Because the strong magnetic field can displace, or disrupt metallic objects, people with an implanted active device like a cardiac pacemaker cannot be scanned under normal circumstances and should not enter the MRI area.
The MRI machine can look like a short tunnel or has an open MRI design and the magnet does not completely surround the patient. Usually the patient lies on a comfortable motorized table, which slides into the scanner, depending on the MRI device, patients may be also able to sit up. If a contrast agent is to be administered, intravenous access will be placed. A technologist will operate the MRI machine and observe the patient during the examination from an adjacent room. Several sets of images are usually required, each taking some minutes. A typical MRI scan includes three to nine imaging sequences and may take up to one hour. Improved MRI devices with powerful magnets, newer software, and advanced sequences may complete the process in less time and better image quality.
Before and after the most MRI procedures no special preparation, diet, reduced activity, and extra medication is necessary. The magnetic field and radio waves are not felt and no pain is to expect.
Movement can blur MRI images and cause certain artifacts. A possible problem is the claustrophobia that some patients experience from being inside a tunnel-like scanner. If someone is very anxious or has difficulty to lie still, a sedative agent may be given. Earplugs and/or headphones are usually given to the patient to reduce the loud acoustic noise, which the machine produces during normal operation. A technologist observes the patient during the test. Some MRI scanners are equipped with televisions and music to help the examination time pass.
MRI is not a cheap examination, however cost effective by eliminating the need for invasive radiographic procedures, biopsies, and exploratory surgery. MRI scans can also save money while minimizing patient risk and discomfort. For example, MRI can reduce the need for X-ray angiography and myelography, and can eliminate unnecessary diagnostic procedures that miss occult disease. See also Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI, Medical Imaging, Cervical Spine MRI, Claustrophobia, MRI Risks and Pregnancy.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Ultrasound Imaging Procedures at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com.
See also the related poll result: ' MRI will have replaced 50% of x-ray exams by' | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Procedure' (11).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Procedure' (6).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Image Quality' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
NAME
Motion, phase encoded motion, instability, smearing
REASON
Movement of the imaged object
HELP
Compensation techniques, more averages, anti spasmodic
Patient motion is the largest physiological effect that causes artifacts, often resulting from involuntary movements (e.g. respiration, cardiac motion and blood flow, eye movements and swallowing) and minor subject movements.
Movement of the object being imaged during the sequence results in inconsistencies in phase and amplitude, which lead to blurring and ghosting. The nature of the artifact depends on the timing of the motion with respect to the acquisition. Causes of motion artifacts can also be mechanical vibrations, cryogen boiling, large iron objects moving in the fringe field (e.g. an elevator), loose connections anywhere, pulse timing variations, as well as sample motion. These artifacts appear in the phase encoding direction, independent of the direction of the motion.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Motion Artifact' (24).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |