 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Joint MRI' found in 0 term [ ] and 0 definition [ ] and 0 definition [ ], (+ 14 Boolean[ ], (+ 14 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| 1 - 5 (of 14) nextResult Pages :  [1 2 3] [1 2 3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Joint MRI' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
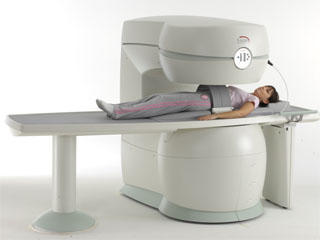
From Esaote S.p.A.;
Esaote introduced the S-SCAN at RSNA in November 2007. The S-SCAN is a dedicated joint and spine MR scanner derived from the company's earlier G-SCAN system. Unlike the G-SCAN, neither the patient table nor
the magnet can rotate from horizontal to vertical position. The patient table can only moved manually. Improved electronics, new coils for lumbar and cervical spine, new pulse sequences, a modified version of the magnet poles and gradient coils are used with a new software release in the S-SCAN.
Esaote North America is the exclusive U.S. distributor of this MRI device.
Device Information and Specification SE, GE, IR, STIR, TSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE POWER REQUIREMENTS 3 kW; 110/220 V single phase | |  | | | | • Share the entry 'S-SCAN':    | | |
• View the NEWS results for 'S-SCAN' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
Standard: head, body, C1, C3; Optional: Small joint, flex-E, flex-R, endocavitary (L and S), dual TMJ, knee, neck, T/L spine, breast; Optional phased array: Spine, pediatric, 3rd party connector, Flex-S-M-L, flex body, flex cardiac, neuro-vascular, head
SE, Modified-SE ( TSE), DAVE, STIR, FLAIR, SPIR, MTC, Dynamic, Keyhole, CLEAR, Q Flow, Balanced FFE, Multi Chunk 3D, Multi Stack 3D, FFE-EPI, SE-EPI, IR-EPI, GRASE, Diffusion Imaging, Perfusion Imaging;; Angiography: Inflow MRA, TONE, PCA, CE MRA
RapidView Recon. greater than 500 @ 256 Matrix
128 x 128, 256 x 256,512 x 512,1024 x 1024
Variable in 1% increments
Lum.: 120 cd/m2; contrast: 150:1
Variable (op. param. depend.)
POWER REQUIREMENTS
380/400 V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Intera 0.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Artirem®, the arthrography-specific contrast agent for MRI is a dilute form of Dotarem® with a less concentration of Gd (1:200).
Artirem® has to be injected directly into the joints for better visualization and delimitation, of the ligament and tendon structures in particular.
Drug Information and Specification
T1, Predominantly positive enhancement
PHARMACOKINETIC
Intravascular, extracellular, renal excretion
CONCENTRATION
0,0025 mmol/ml
PREPARATION
Finished product
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
For sale
PRESENTATION
Pre-filled syringes of 20 mL
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING
PACKAGE INSERT!
Distribution Information
TERRITORY
TRADE NAME
DEVELOPMENT
STAGE
DISTRIBUTOR
France, Switzerland
Artirem®
for sale
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Artirem®' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Joint MRI' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
( MRI) Magnetic resonance imaging is a noninvasive medical imaging technique that uses the interaction between radio frequency pulses, a strong magnetic field and body tissue to obtain images of slices/planes from inside the body. These magnets generate fields from approx. 2000 times up to 30000 times stronger than that of the Earth. The use of nuclear magnetic resonance principles produces extremely detailed pictures of the body tissue without the need for x-ray exposure and gives diagnostic information of various organs.
Measured are mobile hydrogen nuclei (protons are the hydrogen atoms of water, the 'H' in H 20), the majority of elements in the body. Only a small part of them contribute to the measured signal, caused by their different alignment in the magnetic field. Protons are capable of absorbing energy if exposed to short radio wave pulses (electromagnetic energy) at their resonance frequency. After the absorption of this energy, the nuclei release this energy so that they return to their initial state of equilibrium.
This transmission of energy by the nuclei as they return to their initial state is what is observed as the MRI signal. The subtle differing characteristic of that signal from different tissues combined with complex mathematical formulas analyzed on modern computers is what enables MRI imaging to distinguish between various organs. Any imaging plane, or slice, can be projected, and then stored or printed.
The measured signal intensity depends jointly on the spin density and the relaxation times ( T1 time and T2 time), with their relative importance depending on the particular imaging technique and choice of interpulse times. Any motion such as blood flow, respiration, etc. also affects the image brightness.
Magnetic resonance imaging is particularly sensitive in assessing anatomical structures, organs and soft tissues for the detection and diagnosis of a broad range of pathological conditions. MRI pictures can provide contrast between benign and pathological tissues and may be used to stage cancers as well as to evaluate the response to treatment of malignancies. The need for biopsy or exploratory surgery can be eliminated in some cases, and can result in earlier diagnosis of many diseases. See also MRI History and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI' (9).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI' (222).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
A RF coil, often a transmit receive coil with a number of wires running along the z-direction, arranged to give a cosine current variation around the circumference of the coil, which looks like a bird cage.
The bird cage coil works on a different principle to conventionally tuned local and surround coils in that it behaves like a tuned transmission line with one complete cycle of standing wave around the circumference. The frequency supply is generated by an oscillator, which is modulated to form a shaped pulse by a product detector controlled by the waveform generator. The signal must be amplified to 1000's of watts. This can be done using either solid state electronics, valves or a combination of both.
The bird cage coil design provides the best field homogeneity of all RF imaging coils.
One advantage is that it is simple to produce an exceedingly uniform B1 radio frequency field over most of the coil's volume, with the result of images with a high degree of uniformity.
A second advantage is that nodes with zero voltage occur 90° away from the driven part of the coil, thus facilitating the introduction of a second signal in quadrature, which produces a circularly polarized radio frequency field.
This type of volume coil is used for brain (head) MRI, or MR imaging of joints, such as the wrist or knees.
See also the related poll result: ' 3rd party coils are better than the original manufacturer coils' | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Bird Cage Coil' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 14) nextResult Pages :  [1 2 3] [1 2 3] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |