 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | 'Longitudinal Relaxation' | |
Result : Searchterm 'Longitudinal Relaxation' found in 3 terms [ ] and 7 definitions [ ] and 7 definitions [ ], (+ 11 Boolean[ ], (+ 11 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 11 - 15 (of 21) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2]  [3 4 5] [3 4 5] |  | | |  |  |  |
| |
|
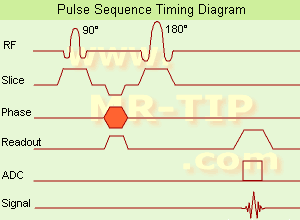
(SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. It uses 90┬░ radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180┬░ pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE).
In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the simplest form of a spin echo sequence is illustrated.
The 90┬░ excitation pulse rotates the longitudinal magnetization ( Mz) into the xy-plane and the dephasing of the transverse magnetization (Mxy) starts.
The following application of a 180° refocusing pulse (rotates the magnetization in the x-plane) generates signal echoes. The purpose of the 180° pulse is to rephase the spins, causing them to regain coherence and thereby to recover transverse magnetization, producing a spin echo.
The recovery of the z-magnetization occurs with the T1 relaxation time and typically at a much slower rate than the T2-decay, because in general T1 is greater than T2 for living tissues and is in the range of 100-2000 ms.
The SE pulse sequence was devised in the early days of NMR days by Carr and Purcell and exists now in many forms: the multi echo pulse sequence using single or multislice acquisition, the fast spin echo (FSE/TSE) pulse sequence, echo planar imaging (EPI) pulse sequence and the gradient and spin echo (GRASE) pulse sequence;; all are basically spin echo sequences.
In the simplest form of SE imaging, the pulse sequence has to be repeated as many times as the image has lines. Contrast values:
PD weighted: Short TE (20 ms) and long TR.
T1 weighted: Short TE (10-20 ms) and short TR (300-600 ms)
T2 weighted: Long TE (greater than 60 ms) and long TR (greater than 1600 ms)
With spin echo imaging no T2* occurs, caused by the 180┬░ refocusing pulse. For this reason, spin echo sequences are more robust against e.g., susceptibility artifacts than gradient echo sequences.
See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram to find a description of the components.
| | | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
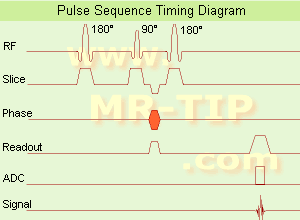
(IR) The inversion recovery pulse sequence produces signals, which represent the longitudinal magnetization existing after the application of a 180┬░ radio frequency pulse that rotates the magnetization Mz into the negative plane. After an inversion time (TI - time between the starting 180┬░ pulse and the following 90┬░ pulse), a further 90┬░ RF pulse tilts some or all of the z-magnetization into the xy-plane, where the signal is usually rephased with a 180┬░ pulse as in the spin echo sequence. During the initial time period, various tissues relax with their intrinsic T1 relaxation time.
In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the basic inversion recovery sequence is illustrated. The 180┬░ inversion pulse is attached prior to the 90┬░ excitation pulse of a spin echo acquisition.
See also the Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram. There you will find a description of the components.
The inversion recovery sequence has the advantage, that it can provide very strong contrast between tissues having different T1 relaxation times or to suppress tissues like fluid or fat.
But the disadvantage is, that the additional inversion radio frequency RF pulse makes this sequence less time efficient than the other pulse sequences.
Contrast values:
PD weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 1800 ms
T1 weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
T2 weighted: TE: 70 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
See also Inversion Recovery, Short T1 Inversion Recovery, Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery, and Acronyms for 'Inversion Recovery Sequence' from different manufacturers. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Inversion Recovery Sequence' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Balanced Fast Field Echo' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  | |  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(MTC) This MRI method increases the contrast by removing a portion of the total signal in tissue. An off resonance radio frequency (RF) pulse saturates macromolecular protons to make them invisible (caused by their ultra-short T2* relaxation times). The MRI signal from semi-solid tissue like brain parenchyma is reduced, and the signal from a more fluid component like blood is retained.
E.g., saturation of broad spectral lines may produce decreases in intensity of lines not directly saturated, through exchange of magnetization between the corresponding states; more closely coupled states will show a greater resulting intensity change.
Magnetization transfer techniques make demyelinated brain or spine lesions (as seen e.g. in multiple sclerosis) better visible on T2 weighted images as well as on gadolinium contrast enhanced T1 weighted images.
Off resonance makes use of a selection gradient during an off resonance MTC pulse. The gradient has a negative offset frequency on the arterial side of the imaging volume (caudally more off resonant and cranially less off resonant). The net effect of this type of pulse is that the arterial blood outside the imaging volume will retain more of its longitudinal magnetization, with more vascular signal when it enters the imaging volume. Off resonance MTC saturates the venous blood, leaving the arterial blood untouched.
On resonance has no effect on the free water pool but will saturate the bound water pool and is the difference in T2 between the pools. Special binomial pulses are transmitted causing the magnetization of the free protons to remain unchanged. The z-magnetization returns to its original value. The spins of the bound pool with a short T2 experience decay, resulting in a destroyed magnetization after the on resonance pulse.
See also Magnetization Transfer. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnetization Transfer Contrast' (5).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |