 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Lumbar Spine MRI' found in 1 term [ ] and 5 definitions [ ] and 5 definitions [ ], (+ 3 Boolean[ ], (+ 3 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 9 (of 9) Result Pages :  [1] [1]  [2] [2] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Lumbar Spine MRI' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview
DESCRIPTION
Loss of signal
HELP
Overlapping prevention
The slice overlap artifact is another name for crosstalk artifact. If slices of multislice acquisitions are overlapping, the spinning nuclei belonging to more than one slice getting multiple times saturated, which leads to signal loss in this areas.

Image Guidance
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
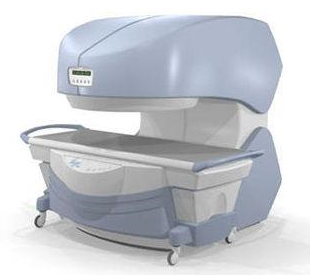
From
Millennium Technology Inc.
This open C-shaped MRI system eases patient comfort and technologist maneuverability. This low cost scanner is build for a wide range of applications. The Virgo™ patient table is detachable and moves on easy rolling castors. Able to accommodate patient weights up to 160 kg, the tabletop has a range of motion of 30 cm in the lateral direction and 90cm in the longitudinal direction. Images generated with this scanner can only be viewed (without data loss) on Millennium's proprietary viewing software.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head, Body, Neck, Knee, Shoulder,
Spine, Wrist, Breast, Extremity, Lumbar Spine, TMJ
IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
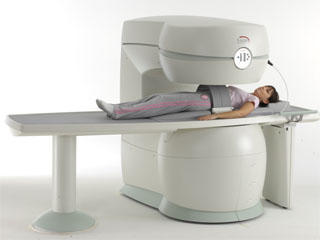
From Esaote S.p.A.;
Esaote introduced the S-SCAN at RSNA in November 2007. The S-SCAN is a dedicated joint and spine MR scanner derived from the company's earlier G-SCAN system. Unlike the G-SCAN, neither the patient table nor
the magnet can rotate from horizontal to vertical position. The patient table can only moved manually. Improved electronics, new coils for lumbar and cervical spine, new pulse sequences, a modified version of the magnet poles and gradient coils are used with a new software release in the S-SCAN.
Esaote North America is the exclusive U.S. distributor of this MRI device.
Device Information and Specification SE, GE, IR, STIR, TSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE POWER REQUIREMENTS 3 kW; 110/220 V single phase | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'S-SCAN' (3).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'S-SCAN' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Lumbar Spine MRI' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Contrast enhanced MRI is a commonly used procedure in magnetic resonance imaging. The need to more accurately characterize different types of lesions and to detect all malignant lesions is the main reason for the use of intravenous contrast agents.
Some methods are available to improve the contrast of different tissues. The focus of dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE- MRI) is on contrast kinetics with demands for spatial resolution dependent on the application. DCE- MR imaging is used for diagnosis of cancer (see also liver imaging, abdominal imaging, breast MRI, dynamic scanning) as well as for diagnosis of cardiac infarction (see perfusion imaging, cardiac MRI). Quantitative DCE- MRI requires special data acquisition techniques and analysis software.
Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) allows the visualization of vessels and the temporal resolution provides a separation of arteries and veins. These methods share the need for acquisition methods with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Double contrast administration (combined contrast enhanced (CCE) MRI) uses two contrast agents with complementary mechanisms e.g., superparamagnetic iron oxide to darken the background liver and gadolinium to brighten the vessels. A variety of different categories of contrast agents are currently available for clinical use.
Reasons for the use of contrast agents in MRI scans are:
•
Relaxation characteristics of normal and pathologic tissues are not always different enough to produce obvious differences in signal intensity.
•
Pathology that is sometimes occult on unenhanced images becomes obvious in the presence of contrast.
•
Enhancement significantly increases MRI sensitivity.
•
In addition to improving delineation between normal and abnormal tissues, the pattern of contrast enhancement can improve diagnostic specificity by facilitating characterization of the lesion(s) in question.
•
Contrast can yield physiologic and functional information in addition to lesion delineation.
Common Indications:
Brain MRI : Preoperative/pretreatment evaluation and postoperative evaluation of brain tumor therapy, CNS infections, noninfectious inflammatory disease and meningeal disease.
Spine MRI : Infection/inflammatory disease, primary tumors, drop metastases, initial evaluation of syrinx, postoperative evaluation of the lumbar spine: disk vs. scar.
Breast MRI : Detection of breast cancer in case of dense breasts, implants, malignant lymph nodes, or scarring after treatment for breast cancer, diagnosis of a suspicious breast lesion in order to avoid biopsy.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com.
See also Blood Pool Agents, Myocardial Late Enhancement, Cardiovascular Imaging, Contrast Enhanced MR Venography, Contrast Resolution, Dynamic Scanning, Lung Imaging, Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents, Contrast Medium and MRI Guided Biopsy. | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast Enhanced MRI' (14).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Enhanced MRI' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
FDA Approves Gadopiclenol for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.pharmacytimes.com |  |  |
Effect of gadolinium-based contrast agent on breast diffusion-tensor imaging
Thursday, 6 August 2020 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Artificial Intelligence Processes Provide Solutions to Gadolinium Retention Concerns
Thursday, 30 January 2020 by www.itnonline.com |  |  |
Accuracy of Unenhanced MRI in the Detection of New Brain Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis
Tuesday, 12 March 2019 by pubs.rsna.org |  |  |
The Effects of Breathing Motion on DCE-MRI Images: Phantom Studies Simulating Respiratory Motion to Compare CAIPIRINHA-VIBE, Radial-VIBE, and Conventional VIBE
Tuesday, 7 February 2017 by www.kjronline.org |  |  |
Novel Imaging Technique Improves Prostate Cancer Detection
Tuesday, 6 January 2015 by health.ucsd.edu |  |  |
New oxygen-enhanced MRI scan 'helps identify most dangerous tumours'
Thursday, 10 December 2015 by www.dailymail.co.uk |  |  |
All-organic MRI Contrast Agent Tested In Mice
Monday, 24 September 2012 by cen.acs.org |  |  |
A groundbreaking new graphene-based MRI contrast agent
Friday, 8 June 2012 by www.nanowerk.com |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |