 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| |
 |
Dear Guest, Your Attention Please: |
|
|
In the next days, the daily page limit for non-members will
decrease to 20 pages to split up resources in favour of the MR-TIP Community.
Beyond this limitation, most resources will still be available for everyone.
If you want to join the MR-TIP Community, please register here.
|
|
| | | |  | Searchterm 'MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
A pacemaker is a device for internal or external battery-operated cardiac pacing to overcome cardiac arrhythmias or heart block. All implanted electronic devices are susceptible to the electromagnetic fields used in magnetic resonance imaging. Therefore, the main magnetic field, the gradient field, and the radio frequency (RF) field are potential hazards for cardiac pacemaker patients.
The pacemaker's susceptibility to static field and its critical role in life support have warranted special consideration. The static magnetic field applies force to magnetic materials. This force and torque effects rise linearly with the field strength of the MRI machines. Both, RF fields and pulsed gradients can induce voltages in circuits or on the pacing lead, which will heat up the tissue around e.g. the lead tip, with a potential risk of thermal injury.
Regulations for pacemakers provide that they have to switch to the magnet mode in static magnetic fields above 1.0 mT. In MR imaging, the gradient and RF fields may mimic signals from the heart with inhibition or fast pacing of the heart. In the magnet mode, most of the current pacemakers will pace with a fix pulse rate because they do not accept the heartsignals. However, the state of an implanted pacemaker will be unpredictable inside a strong magnetic field. Transcutaneous controller adjustment of pacing rate is a feature of many units. Some achieve this control using switches activated by the external application of a magnet to open/close the switch. Others use rotation of an external magnet to turn internal controls. The fringe field around the MRI magnet can activate such switches or controls. Such activations are a safety risk.
Areas with fields higher than 0.5 mT ( 5 Gauss Limit) commonly have restricted access and/or are posted as a safety risk to persons with pacemakers.

A Cardiac pacemaker is because the risks, under normal circumstances an absolute contraindication for MRI procedures.
Nevertheless, with special precaution the risks can be lowered. Reprogramming the pacemaker to an asynchronous mode with fix pacing rate or turning off will reduce the risk of fast pacing or inhibition. Reducing the SAR value reduces the potential MRI risks of heating. For MRI scans of the head and the lower extremities, tissue heating also seems to be a smaller problem. If a transmit receive coil is used to scan the head or the feet, the cardiac pacemaker is outside the sending coil and possible heating is very limited. | |  | | • For this and other aspects of MRI safety see our InfoSheet about MRI Safety. | | | • Patient-related information is collected in our MRI Patient Information.
| | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
A psychological reaction to being confined in a relatively small area.
This is a very real psychological danger for some individuals during the MRI procedure. A small percentage of patients is claustrophobic and cannot tolerate the confined space within a closed MRI magnet. Claustrophobia, panic attacks and other psychological stress situations have been reported in about 1-4% of cases as a reason to interrupt the MRI examination. Principally short and wide open MRI devices are advantageous because the percentage of claustrophobic incidents drops significantly.
Detailed explanation of the MRI procedure, careful attention and special equipment (mirrors to look outside the machine, emergency bells) help to reduce claustrophobia significantly. The majority of claustrophobic patients will be sufficiently relaxed with orally or intravenous sedatives. See also Open MRI. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Claustrophobia' (16).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | MRI Safety Resources | | | | |
|  |  |  |
| |
|
Contrast agents are chemical substances introduced to the anatomical or functional region being imaged, to increase the differences between different tissues or between normal and abnormal tissue, by altering the relaxation times. MRI contrast agents are classified by the different changes in relaxation times after their injection.
•
Negative contrast agents (appearing predominantly dark on MRI) are small particulate aggregates often termed superparamagnetic iron oxide ( SPIO). These agents produce predominantly spin spin relaxation effects (local field inhomogeneities), which results in shorter T1 and T2 relaxation times.
SPIO's and ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides ( USPIO) usually consist of a crystalline iron oxide core containing thousands of iron atoms and a shell of polymer, dextran, polyethyleneglycol, and produce very high T2 relaxivities. USPIOs smaller than 300 nm cause a substantial T1 relaxation. T2 weighted effects are predominant.
•
A special group of negative contrast agents (appearing dark on MRI) are perfluorocarbons ( perfluorochemicals), because their presence excludes the hydrogen atoms responsible for the signal in MR imaging.
The design objectives for the next generation of MR contrast agents will likely focus on prolonging intravascular retention, improving tissue targeting, and accessing new contrast mechanisms. Macromolecular paramagnetic contrast agents are being tested worldwide. Preclinical data shows that these agents demonstrate great promise for improving the quality of MR angiography, and in quantificating capillary permeability and myocardial perfusion.
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide ( USPIO) particles have been evaluated in multicenter clinical trials for lymph node MR imaging and MR angiography, with the clinical impact under discussion. In addition, a wide variety of vector and carrier molecules, including antibodies, peptides, proteins, polysaccharides, liposomes, and cells have been developed to deliver magnetic labels to specific sites. Technical advances in MR imaging will further increase the efficacy and necessity of tissue-specific MRI contrast agents.
See also Adverse Reaction and Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis.
See also the related poll result: ' The development of contrast agents in MRI is' | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast Agents' (122).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Agents' (25).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Brain imaging method may aid mild traumatic brain injury diagnosis
Tuesday, 16 January 2024 by parkinsonsnewstoday.com |  |  |
A Targeted Multi-Crystalline Manganese Oxide as a Tumor-Selective Nano-Sized MRI Contrast Agent for Early and Accurate Diagnosis of Tumors
Thursday, 18 January 2024 by www.dovepress.com |  |  |
FDA Approves Gadopiclenol for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.pharmacytimes.com |  |  |
How to stop using gadolinium chelates for magnetic resonance imaging: clinical-translational experiences with ferumoxytol
Saturday, 5 February 2022 by www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
Estimation of Contrast Agent Concentration in DCE-MRI Using 2 Flip Angles
Tuesday, 11 January 2022 by pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
Manganese enhanced MRI provides more accurate details of heart function after a heart attack
Tuesday, 11 May 2021 by www.news-medical.net |  |  |
Gadopiclenol: positive results for Phase III clinical trials
Monday, 29 March 2021 by www.pharmiweb.co |  |  |
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents Hypersensitivity: A Case Series
Friday, 4 December 2020 by www.dovepress.com |  |  |
Polysaccharide-Core Contrast Agent as Gadolinium Alternative for Vascular MR
Monday, 8 March 2021 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Water-based non-toxic MRI contrast agents
Monday, 11 May 2020 by chemistrycommunity.nature.com |  |  |
New method to detect early-stage cancer identified by Georgia State, Emory research team
Friday, 7 February 2020 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Researchers Brighten Path for Creating New Type of MRI Contrast Agent
Friday, 7 February 2020 by www.newswise.com |  |  |
Manganese-based MRI contrast agent may be safer alternative to gadolinium-based agents
Wednesday, 15 November 2017 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Sodium MRI May Show Biomarker for Migraine
Friday, 1 December 2017 by psychcentral.com |  |  |
A natural boost for MRI scans
Monday, 21 October 2013 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
For MRI, time is of the essence A new generation of contrast agents could make for faster and more accurate imaging
Tuesday, 28 June 2011 by scienceline.org |
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Lung Imaging' (7).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Lung Imaging' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Chest MRI a viable alternative to chest CT in COVID-19 pneumonia follow-up
Monday, 21 September 2020 by www.healthimaging.com |  |  |
CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Corona virus (2019-nCoV)
Tuesday, 4 February 2020 by pubs.rsna.org |  |  |
Polarean Imaging Phase III Trial Results Point to Potential Improvements in Lung Imaging
Wednesday, 29 January 2020 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Low Power MRI Helps Image Lungs, Brings Costs Down
Thursday, 10 October 2019 by www.medgadget.com |  |  |
Chest MRI Using Multivane-XD, a Novel T2-Weighted Free Breathing MR Sequence
Thursday, 11 July 2019 by www.sciencedirect.co |  |  |
Researchers Review Importance of Non-Invasive Imaging in Diagnosis and Management of PAH
Wednesday, 11 March 2015 by lungdiseasenews.com |  |  |
New MRI Approach Reveals Bronchiectasis' Key Features Within the Lung
Thursday, 13 November 2014 by lungdiseasenews.com |  |  |
MRI techniques improve pulmonary embolism detection
Monday, 19 March 2012 by medicalxpress.com |
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'MRI' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
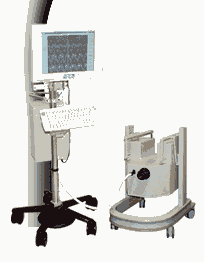
From MagneVu;
The MagneVu 1000 is a compact, robust, and portable, permanent magnet MRI system and operates without special shielding or costly site preparation.
This MRI device utilizes a patented non-homogeneous magnetic field image acquisition method to achieve high performance imaging. The MagneVu 1000 MRI scanner is designed for MRI of the extremities with the current specialty areas in diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Easy access is afforded for claustrophobic, pediatric, or limited mobility patients. In August 1998
FDA marketing clearance and other regulatory approvals have been received. Until 2008, over 130 devices in the US are in use. Some further developments of MagneVu's extremity scanner are: 'truly Plug n' Play MRI™' and iSiS ( which adds wireless capability to the second generation MV1000-XL).
Device Information and Specification IMAGING MODES 3-dimensional multi-echo data acquisition | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MagneVu 1000' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |