 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Magnet' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| Magnet |  |
| |
|
A magnet is by definition an object with magnetic properties ( magnetism) that attracts iron and produces a magnetic field. It can be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet.
Permanent magnets do not rely upon outside influences to generate their field. In permanent magnets are the atoms and molecules ordered in long range. The specific electron configuration and the distance of the atoms is what lead to this long range ordering. The electrons exist in a lower energy state if they all have the same orientation. Magnetic domains can be likened to microscopic neighborhoods in which there is a strong reinforcing interaction between particles, resulting in a high degree of order. The greater the degree of ordering within and between domains, the greater the resulting field will be. Long range ordering is one of the hallmarks of a ferromagnetic material.
A current carrying conductor for example a piece of wire, produces a magnetic field that encircles the wire. An electromagnet, in its simplest form, is a wire that has been coiled into one or more loops. This coil is known as a solenoid. The more loops of wire and the greater the current, the stronger the field will be.
Superconducting magnets are a special type of electro magnets, often used in MRI machines with high field strength. | |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Magnet':    | | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Magnet' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Magnetic forces are fundamental forces that arise due to the movement of electrical charge. Maxwell's equations describe the origin and behavior of the fields that govern these forces. Thus, magnetism is seen whenever electrically charged particles are in motion. This can arise either from movement of electrons in an electric current, resulting in 'electro magnetism', or from the quantum-mechanical orbital motion (there is no orbital motion of electrons around the nucleus like planets around the sun, but there is an 'effective electron velocity') and spin of electrons, resulting in what are known as ' permanent magnets'.
The physical cause of the magnetism of objects, as distinct from electrical currents, is the atomic magnetic dipole. Magnetic dipoles, or magnetic moments, result on the atomic scale from the two kinds of movement of electrons. The first is the orbital motion of the electron around the nucleus this motion can be considered as a current loop, resulting in an orbital dipole magnetic moment along the axis of the nucleus. The second, much stronger, source of electronic magnetic moment is due to a quantum mechanical property called the spin dipole magnetic moment.
Gauss (G) and tesla (T) are units to define the intensity of magnetic fields. One tesla is equivalent to 10 000 gauss.
Typically, the field strength of MRI scanners is between 0.15 T and 3 T.
See also Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Superparamagnetism, and Ferromagnetism. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnetism' (18).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Magnetism' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Magnet' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
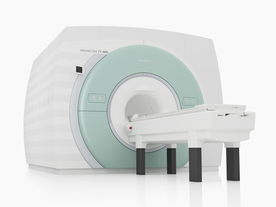
From Siemens Medical Systems;
The MAGNETOM 7T is designed as an open research platform. 7T MRI provides anatomical detail at the submillimiter scale, enhanced contrast mechanisms, outstanding spectroscopy performance, ultra-high resolution functional imaging ( fMRI), multinuclear whole-body MRI and functional information.
This ultra high field (UHF) MRI device is a research system and not cleared, approved or licensed in any jurisdiction for patient examinations.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
High-performance, ultra high field coils available. Integration and support for coil developments.
CHANNELS (min. / max. configuration)
32, optional 8 channels TX array
40 x 40 x 30 cm³ less than 8% nonlinearity
MAGNET WEIGHT (gantry included)
35017 kg
DIMENSION H*W*D (gantry included)
320 x 240 x 317,5 cm
MAX. AMPLITUDE
up to 70 mT/m
Up to 3rd order shim coils, user configurable B0 shim ? B0 maps and ROI definition
POWER REQUIREMENTS
2000 Volts, 650A
| |  | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Magnet' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
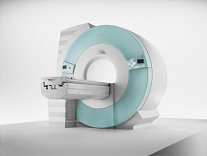
From Siemens Medical Systems;
70 cm + 125 cm + 1.5T and Tim - a combination never seen before in MRI ...
MAGNETOM Espree™s unique open bore design can accommodate more types of patients than other 1.5T systems on the market today, in particular the growing population of obese patients. The power of 1.5T combined with Tim technology boosts signal to noise, which is necessary to adequately image obese patients.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Body, Tim [32 x 8], Tim [76 coil elements with up to 18 RF channels])
GRE, IR, FIR, STIR, TrueIR/FISP, FSE, FLAIR, MT, SS-FSE, MT-SE, MTC, MSE, EPI, 3D DESS//CISS/PSIF, GMR
IMAGING MODES
Single, multislice, volume study, multi angle, multi oblique
Image Processor reconstructing up to 3226 images per second (256 x 256, 25% recFoV)
1024 x 1024 full screen display
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MAGNETOM Espree™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |