 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Multi Echo Imaging' found in 1 term [ ] and 2 definitions [ ] and 2 definitions [ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ], (+ 19 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 22) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Multi Echo Imaging' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
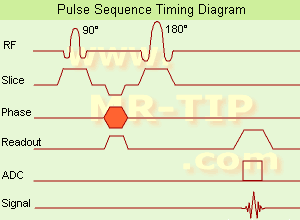
(SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. It uses 90┬░ radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180┬░ pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE).
In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the simplest form of a spin echo sequence is illustrated.
The 90┬░ excitation pulse rotates the longitudinal magnetization ( Mz) into the xy-plane and the dephasing of the transverse magnetization (Mxy) starts.
The following application of a 180° refocusing pulse (rotates the magnetization in the x-plane) generates signal echoes. The purpose of the 180° pulse is to rephase the spins, causing them to regain coherence and thereby to recover transverse magnetization, producing a spin echo.
The recovery of the z-magnetization occurs with the T1 relaxation time and typically at a much slower rate than the T2-decay, because in general T1 is greater than T2 for living tissues and is in the range of 100-2000 ms.
The SE pulse sequence was devised in the early days of NMR days by Carr and Purcell and exists now in many forms: the multi echo pulse sequence using single or multislice acquisition, the fast spin echo (FSE/TSE) pulse sequence, echo planar imaging (EPI) pulse sequence and the gradient and spin echo (GRASE) pulse sequence;; all are basically spin echo sequences.
In the simplest form of SE imaging, the pulse sequence has to be repeated as many times as the image has lines. Contrast values:
PD weighted: Short TE (20 ms) and long TR.
T1 weighted: Short TE (10-20 ms) and short TR (300-600 ms)
T2 weighted: Long TE (greater than 60 ms) and long TR (greater than 1600 ms)
With spin echo imaging no T2* occurs, caused by the 180┬░ refocusing pulse. For this reason, spin echo sequences are more robust against e.g., susceptibility artifacts than gradient echo sequences.
See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram to find a description of the components.
| | | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
From Aurora Imaging Technology, Inc.;
The Aurora┬« 1.5T Dedicated Breast MRI System with Bilateral SpiralRODEO™ is the first and only FDA approved MRI device designed specifically for breast imaging. The Aurora System, which is already in clinical use at a growing number of leading breast care centers in the US, Europe, got in December 2006 also the approval from the State Food and Drug Administration of the People's Republic of China (SFDA).
'Some of the proprietary and distinguishing features of the Aurora System include: 1) an ellipsoid magnetic shim that provides coverage of both breasts, the chest wall and bilateral axillary lymph nodes; 2) a precision gradient coil with the high linearity required for high resolution spiral reconstruction;; 3) a patient-handling table that provides patient comfort and procedural utility; 4) a fully integrated Interventional System for MRI guided biopsy and localization; and 5) the user-friendly AuroraCADÔäó computer-aided image display system designed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic interpretations.'
Device Information and Specification
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
TE
From 5 ms for RODEO Plus to over 80 ms, 120 ms for T2 sequences
Around 0.02 sec for a 256x256 image, 12.4 sec for a 512 x 512 x 32 multislice set
20 - 36 cm, max. elliptical 36 x 44 cm
POWER REQUIREMENTS
150A/120V-208Y/3 Phase//60 Hz/5 Wire
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Aurora® 1.5T Dedicated Breast MRI System' (2).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Aurora┬« 1.5T Dedicated Breast MRI System' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
SE, IR, FSE, FIR, GE, SG, BASG, PBSG, PCIR, DWI, Radial, Angiography: TOF, FLUTE (Fluoro-triggered bolus MRA), Time-resolved MRA
IMAGING MODES
Single, multislice, volume study
Level Range: -2,000 to +4,000
POWER REQUIREMENTS
208/220/240 V, single phase
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Echelon™ 1.5T' (2).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'EchelonÔäó 1.5T' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Multi Echo Imaging' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
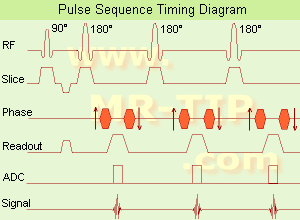
(FSE) In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast spin echo sequence with an echo train length of 3 is illustrated.
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180° rephasing pulses and multiple echoes, changing the phase encoding gradient for each echo.
The echo time TE may vary from echo to echo in the echo train. The echoes in the center of the K-space (in the case of linear k-space acquisition) mainly produce the type of image contrast, whereas the periphery of K-space determines the spatial resolution. For example, in the middle of K-space the late echoes of T2 weighted images are encoded. T1 or PD contrast is produced from the early echoes.
The benefit of this technique is that the scan duration with, e.g. a turbo spin echo turbo factor / echo train length of 9, is one ninth of the time. In T1 weighted and proton density weighted sequences, there is a limit to how large the ETL can be (e.g. a usual ETL for T1 weighted images is between 3 and 7). The use of large echo train lengths with short TE results in blurring and loss of contrast. For this reason, T2 weighted imaging profits most from this technique.
In T2 weighted FSE images, both water and fat are hyperintense. This is because the succession of 180° RF pulses reduces the spin spin interactions in fat and increases its T2 decay time. Fast spin echo (FSE) sequences have replaced conventional T2 weighted spin echo sequences for most clinical applications. Fast spin echo allows reduced acquisition times and enables T2 weighted breath hold imaging, e.g. for applications in the upper abdomen.
In case of the acquisition of 2 echoes this type of a sequence is named double fast spin echo / dual echo sequence, the first echo is usually density and the second echo is T2 weighted image. Fast spin echo images are more T2 weighted, which makes it difficult to obtain true proton density weighted images. For dual echo imaging with density weighting, the TR should be kept between 2000 - 2400 msec with a short ETL (e.g., 4).
Other terms for this technique are:
Turbo Spin Echo
Rapid Imaging Spin Echo,
Rapid Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fast Spin Echo' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
From
Millennium Technology Inc.
This open C-shaped MRI system eases patient comfort and technologist maneuverability. This low cost scanner is build for a wide range of applications. The Virgo™ patient table is detachable and moves on easy rolling castors. Able to accommodate patient weights up to 160 kg, the tabletop has a range of motion of 30 cm in the lateral direction and 90cm in the longitudinal direction. Images generated with this scanner can only be viewed (without data loss) on Millennium's proprietary viewing software.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head, Body, Neck, Knee, Shoulder,
Spine, Wrist, Breast, Extremity, Lumbar Spine, TMJ
IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multislice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |