|
Magnetic
Resonance -
Technology
Information
Portal |
Welcome to MRI Technology • • |
|
|
 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | 'Partial Volume Artifact' | |
Result : Searchterm 'Partial Volume Artifact' found in 1 term [ ] and 3 definitions [ ] and 3 definitions [ ] ]
| 1 - 4 (of 4) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |  | | |  |  |  |
| Partial Volume Artifact |  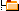 |
| |
|
Quick Overview
DESCRIPTION
Loss of contrast between two adjacent tissues
The Partial Volume Artifact is caused by imaging voxel containing two different tissues and therefore possessing a signal average of both tissues.

Image Guidance
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Partial Volume Artifact':    | | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Partial Volume Artifact' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
This happens whenever a structure is only partly within the imaging section, pixel or voxel. The consequence is that the signals of the structure and the adjacent or surrounding structures present in the section, pixel or voxel are averaged.
As a result erroneous pixel or voxel signal values result. This can lead to diagnostic misinterpretations.
See also Partial Volume Artifact. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Partial Volume Averaging' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
The partial volume effect is the loss of contrast between two adjacent tissues in an image caused by insufficient resolution so that more than one tissue type occupies the same voxel (or pixel). That may induce a partial volume artifact, dependent on the size of the image voxel. If fat and water spins occupy the same voxel, their signals interfere destructively. A small amount of water signal may be eliminated by a larger lipid signal from the same voxel, resulting in a voxel that appears to contain only lipid. The partial volume effect is minimal with thin slice thickness and sufficiently high resolution, so that fat and water or other different structures are unlikely to occupy the same voxel.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Partial Volume Effect' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(THK) The thickness of an imaging slice. As the slice profile may not be sharp edged, a criterion such as the distance between the points at half the sensitivity of the maximum (FWHM) or the equivalent rectangular width (the width of a rectangular slice profile with the same maximum height and same area) is used to determine thickness.

Image Guidance
For the image quality its important to choose the best fitting slice thickness for an examination. When a small item is entirely contained within the slice thickness with other tissue of differing signal intensity then the resulting signal displayed on the image is a combination of these two intensities. If the slice is the same thickness or thinner than the small structure, only that structures signal intensity is displayed on the image. This partial volume averaging effect explains the vanishing of
fine details by choosing slices too large for the scanned object.
See also Partial Volume Artifact. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Slice Thickness' (63).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Partial Volume Artifact' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |
|  | |
|  | 1 - 4 (of 4) Result Pages :  [1] [1] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |
|
MR-TIP.com uses cookies! By browsing MR-TIP.com, you agree to our use of cookies. | | | [last update: 2024-02-26 03:41:00] |
|
|