 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Planar Imaging' found in 5 terms [ ] and 15 definitions [ ] and 15 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 6 - 10 (of 20) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4] [2 3 4] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Planar Imaging' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  | |  |  | Searchterm 'Planar Imaging' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
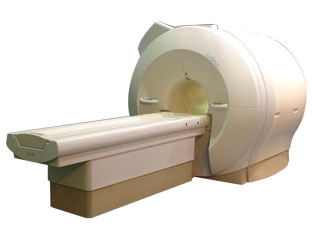
'Next generation MRI system 1.5T CHORUS developed by ISOL Technology is optimized for both clinical diagnostic imaging and for research development.
CHORUS offers the complete range of feature oriented advanced imaging techniques- for both clinical routine and research. The compact short bore magnet, the patient friendly design and the gradient technology make the innovation to new degree of perfection in magnetic resonance.'
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
Spin Echo, Gradient Echo, Fast Spin Echo,
Inversion Recovery ( STIR, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery), FLASH, FISP, PSIF, Turbo Flash ( MPRAGE ),TOF MR Angiography, Standard echo planar imaging package (SE-EPI, GE-EPI), Optional:
Advanced P.A. Imaging Package (up to 4 ch.), Advanced echo planar imaging package,
Single Shot and Diffusion Weighted EPI, IR/FLAIR EPI
STRENGTH
20 mT/m (Upto 27 mT/m)
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'CHORUS 1.5T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Burst pulse sequences are fast imaging sequences capable of image acquisition in less than 100 ms.
Basically a train of low flip angle pulses generates a long train of echoes. The complete sequence is performed with the application of a constant read gradient. Phase encoding may be implemented using short phase encoding gradients between echoes.
The advantage of this sequence type is that it is less demanding on gradient speed than other fast techniques (e.g. echo planar imaging EPI) and it produces images, which are substantially free of susceptibility artifacts.
The disadvantage is that the technique is less sensitive than competing methods. | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Planar Imaging' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
This method synchronize the heartbeat with the beginning of the TR, whereat the r wave is used as the trigger. Cardiac gating times the acquisition of MR data to physiological motion in order to minimize motion artifacts. ECG gating techniques are useful whenever data acquisition is too slow to occur during a short fraction of the cardiac cycle.
Image blurring due to cardiac-induced motion occurs for imaging times of above approximately 50 ms in systole, while for imaging during diastole the critical time is of the order of 200-300 ms. The acquisition of an entire image in this time is only possible with using ultrafast MR imaging techniques. If a series of images using cardiac gating or real-time echo planar imaging EPI are acquired over the entire cardiac cycle, pixel-wise velocity and vascular flow can be obtained.
In simple cardiac gating, a single image line is acquired in each cardiac cycle. Lines for multiple images can then be acquired successively in consecutive gate intervals. By using the standard multiple slice imaging and a spin echo pulse sequence, a number of slices at different anatomical levels is obtained. The repetition time (TR) during a ECG-gated acquisition equals the RR interval, and the RR interval defines the minimum possible repetition time (TR). If longer TRs are required, multiple integers of the RR interval can be selected. When using a gradient echo pulse sequence, multiple phases of a single anatomical level or multiple slices at different anatomical levels can be acquired over the cardiac cycle.
Also called cardiac triggering. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Cardiac Gating' (15).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Planar Imaging' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(DWI) Magnetic resonance imaging is sensitive to diffusion, because the diffusion of water molecules along a field gradient reduces the MR signal. In areas of lower diffusion the signal loss is less intense and the display from this areas is brighter. The use of a bipolar gradient pulse and suitable pulse sequences permits the acquisition of diffusion weighted images (images in which areas of rapid proton diffusion can be distinguished from areas with slow diffusion).
Based on echo planar imaging, multislice DWI is today a standard for imaging brain infarction. With enhanced gradients, the whole brain can be scanned within seconds. The degree of diffusion weighting correlates with the strength of the diffusion gradients, characterized by the b-value, which is a function of the gradient related parameters: strength, duration, and the period between diffusion gradients.
Certain illnesses show restrictions of diffusion, for example demyelinization and cytotoxic edema. Areas of cerebral infarction have decreased apparent diffusion, which results in increased signal intensity on diffusion weighted MRI scans. DWI has been demonstrated to be more sensitive for the early detection of stroke than standard pulse sequences and is closely related to temperature mapping.
DWIBS is a new diffusion weighted imaging technique for the whole body that produces PET-like images. The DWIBS sequence has been developed with the aim to detect lymph nodes and to differentiate normal and hyperplastic from metastatic lymph nodes. This may be possible caused by alterations in microcirculation and water diffusivity within cancer metastases in lymph nodes.
See also Diffusion Weighted Sequence, Perfusion Imaging, ADC Map, Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, and Diffusion Tensor Imaging. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Diffusion Weighted Imaging' (11).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Diffusion Weighted Imaging' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |