 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Proton' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Contrast is the relative difference of signal intensities in two adjacent regions of an image.
Due to the T1 and T2 relaxation properties in magnetic resonance imaging, differentiation between various tissues in the body is possible. Tissue contrast is affected by not only the T1 and T2 values of specific tissues, but also the differences in the magnetic field strength, temperature changes, and many other factors. Good tissue contrast relies on optimal selection of appropriate pulse sequences ( spin echo, inversion recovery, gradient echo, turbo sequences and slice profile).
Important pulse sequence parameters are TR ( repetition time), TE (time to echo or echo time), TI (time for inversion or inversion time) and flip angle. They are associated with such parameters as proton density and T1 or T2 relaxation times. The values of these parameters are influenced differently by different tissues and by healthy and diseased sections of the same tissue.
For the T1 weighting it is important to select a correct TR or TI. T2 weighted images depend on a correct choice of the TE. Tissues vary in their T1 and T2 times, which are manipulated in MRI by selection of TR, TI, and TE, respectively. Flip angles mainly affect the strength of the signal measured, but also affect the TR/TI/TE parameters.
Conditions necessary to produce different weighted images:
T1 Weighted Image: TR value equal or less than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value less than the tissue specific T2 time.
T2 Weighted Image: TR value much greater than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value greater or equal than the tissue specific T2 time.
Proton Density Weighted Image: TR value much greater than the tissue specific T1 time - TE value less than the tissue specific T2 time.
See also Image Contrast Characteristics, Contrast Reversal, Contrast Resolution, and Contrast to Noise Ratio. | | | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Proton' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
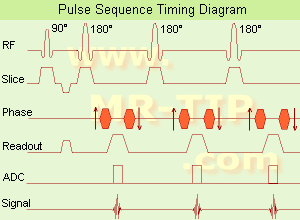
(FSE) In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast spin echo sequence with an echo train length of 3 is illustrated.
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180° rephasing pulses and multiple echoes, changing the phase encoding gradient for each echo.
The echo time TE may vary from echo to echo in the echo train. The echoes in the center of the K-space (in the case of linear k-space acquisition) mainly produce the type of image contrast, whereas the periphery of K-space determines the spatial resolution. For example, in the middle of K-space the late echoes of T2 weighted images are encoded. T1 or PD contrast is produced from the early echoes.
The benefit of this technique is that the scan duration with, e.g. a turbo spin echo turbo factor / echo train length of 9, is one ninth of the time. In T1 weighted and proton density weighted sequences, there is a limit to how large the ETL can be (e.g. a usual ETL for T1 weighted images is between 3 and 7). The use of large echo train lengths with short TE results in blurring and loss of contrast. For this reason, T2 weighted imaging profits most from this technique.
In T2 weighted FSE images, both water and fat are hyperintense. This is because the succession of 180° RF pulses reduces the spin spin interactions in fat and increases its T2 decay time. Fast spin echo (FSE) sequences have replaced conventional T2 weighted spin echo sequences for most clinical applications. Fast spin echo allows reduced acquisition times and enables T2 weighted breath hold imaging, e.g. for applications in the upper abdomen.
In case of the acquisition of 2 echoes this type of a sequence is named double fast spin echo / dual echo sequence, the first echo is usually density and the second echo is T2 weighted image. Fast spin echo images are more T2 weighted, which makes it difficult to obtain true proton density weighted images. For dual echo imaging with density weighting, the TR should be kept between 2000 - 2400 msec with a short ETL (e.g., 4).
Other terms for this technique are:
Turbo Spin Echo
Rapid Imaging Spin Echo,
Rapid Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fast Spin Echo' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(FAT SAT) A specialized technique that selectively saturates fat protons prior to acquiring data as in standard sequences, so that they produce a negligible signal. The presaturation pulse is applied prior to each slice selection. This technique requires a very homogeneous magnetic field and very precise frequency calibration.
Fat saturation does not work well on inhomogeneous volumes of tissue due to a change in the precessional frequencies as the difference in volume affects the magnetic field homogeneity. The addition of a water bag simulates a more homogeneous volume of tissue, thus improving the fat saturation. Since the protons in the water bag are in motion due to recent motion of the bag, phase ghosts can be visualized.
Fat saturation can also be difficult in a region of metallic prosthesis. This is caused by an alteration in the local magnetic field resulting in a change to the precessional frequencies, rendering the chemical saturation pulses ineffective.
See also Fat Suppression, and Dixon. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fat Saturation' (9).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Proton' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Fat suppression is the process of utilizing specific MRI parameters to remove the deleterious effects of fat from the resulting images , e.g. with STIR, FAT SAT sequences, water selective (PROSET WATS - water only selection, also FATS - fat only selection possible) excitation techniques, or pulse sequences based on the Dixon method.
Spin magnetization can be modulated by using special RF pulses. CHESS or its variations like SPIR, SPAIR ( Spectral Selection Attenuated Inversion Recovery) and FAT SAT use frequency selective excitation pulses, which produce fat saturation.
Fat suppression techniques are nearly used in all body parts and belong to every standard MRI protocol of joints like knee, shoulder, hips, etc.

Image Guidance
Imaging of, e.g. the foot can induce bad fat suppression with SPIR/FAT SAT due to the asymmetric volume of this body part. The volume of the foot alters the magnetic field to a different degree than the smaller volume of the lower leg affecting the protons there. There is only a small band of tissue where the fat protons are precessing at the frequency expected, resulting in frequency selective fat saturation working only in that area. This can be corrected by volume shimming or creating a more symmetrical volume being imaged with water bags.
Even with their longer scan time and motion sensitivity, STIR (short T1/tau inversion recovery) sequences are often the better choice to suppress fat. STIR images are also preferred because of the decreased sensitivity to field inhomogeneities, permitting larger fields of views when compared to fat suppressed images and the ability to image away from the isocenter. See also Knee MRI.
Sequences based on Dixon turbo spin echo ( fast spin echo) can deliver a significant better fat suppression than conventional TSE/FSE imaging.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fat Suppression' (28).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Proton' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Perflubron® is a perfluorochemical for use as an oral contrast agent. Due to its insolubility in water it does not mix with intestinal secretions; thus bowel lumina appear homogeneously dark on MR images when Perflubron® replaces bowel contents. Filled bowel loops appear black with all pulse sequences because the contrast agent lacks mobile protons.
It is commercially available as Imagent GI. Because rapid transit through the gastrointestinal tract it reaches the rectum within 30 to 40 minutes in most patients. MR imaging of the upper abdominal region should begin within 15 minutes and of the pelvic region 15 to 60 minutes after ingestion of perflubron.
See also Classifications, Characteristics, etc.
Drug Information and Specification
NAME OF COMPOUND
Perfluoroctylbromide
PHARMACOKINETIC
Gastrointestinal
CONCENTRATION
Water immiscible liquid
DOSAGE
9 mL per kg of body weight
PREPARATION
Finished product
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
For sale
PRESENTATION
Bottle of 200cc
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING
PACKAGE INSERT!
Distribution Information
TERRITORY
TRADE NAME
DEVELOPMENT
STAGE
DISTRIBUTOR
USA
Imagent GI®
For sale
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Imagent GI' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |