In simple ultrafast GRE imaging, TR and TE are so short, that tissues have a poor imaging signal and - more importantly - poor
contrast except when
contrast media enhanced (
contrast enhanced
angiography). Therefore, the
magnetization is 'prepared' during the preparation module, most frequently by an initial
180°
inversion pulse.
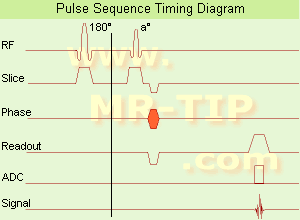
In the
pulse sequence timing diagram, the basic ultrafast
gradient echo sequence is illustrated. The
180°
inversion pulse is executed one time (to the left of the vertical line), the right side represents the data collection period and is often repeated depending on the acquisition parameters.
See also
Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, there you will find a description of the components.
Ultrafast GRE
sequences have a short TR,TE, a low
flip angle and TR is so short that image acquisition lasts less than 1
second and typically less than 500 ms. Common TR: 3-5 msec, TE: 2 msec, and the
flip angle is about 5°.
Such
sequences are often labeled with the prefix 'Turbo' like
TurboFLASH, TurboFFE and TurboGRASS.
This allows one to center the subsequent ultrafast GRE data acquisition around the
inversion time TI, where one of the tissues of interest has very little signal as its z-magnetization is passing through zero.
Unlike a standard
inversion recovery (IR) sequence, all lines or a substantial segment of
k-space image lines are acquired after a single
inversion pulse, which can then together be considered as readout module. The readout module may use a
variable flip angle approach, or the data acquisition may be divided into multiple segments (shots). The latter is useful particularly in
cardiac imaging where acquiring all lines in a single segment may take too long relative to the
cardiac cycle to provide adequate
temporal resolution.
If multiple lines are acquired after a single
pulse, the
pulse sequence is a type of
gradient echo echo planar imaging (EPI)
pulse sequence.
See also
Magnetization Prepared Rapid Gradient Echo (
MPRAGE) and
Turbo Field Echo (
TFE).