 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
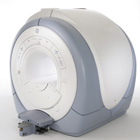
From GE Healthcare;
The Signa HDx MRI system is GE's leading edge whole body magnetic resonance scanner designed to support high resolution, high signal to noise ratio, and short scan times.
Signa HDx 3.0T offers new technologies like ultra-fast image reconstruction through the new XVRE recon engine, advancements in parallel imaging algorithms and the broadest range of premium applications. The HD applications, PROPELLER (high-quality brain imaging extremely resistant to motion artifacts), TRICKS (contrast-enhanced angiographic vascular lower leg imaging), VIBRANT (for breast MRI), LAVA (high resolution liver imaging with shorter breath holds and better organ coverage) and MR Echo (high-definition cardiac images in real time) offer unique capabilities.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body
CONFIGURATION Compact short bore SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE, RF-spoiled GRE, 2DFGRE, 2DFSPGR, 3DFGRE, 3DFSPGR, 3DTOFGRE, 3DFSPGR, 2DFSE, 2DFSE-XL, 2DFSE-IR, T1-FLAIR, SSFSE, EPI, DW-EPI, BRAVO, Angiography: 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D phase contrast vascular IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, fast scan, multi slab, cine, localizer H*W*D 240 x 2216,6 x 201,6 cm POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415, 3 phase ||
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled grad. | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
( SNR or S/N) The signal to noise ratio is used in MRI to describe the relative contributions to a detected signal of the true signal and random superimposed signals ('background noise') - a criterion for image quality.
One common method to increase the SNR is to average several measurements of the signal, on the expectation that random contributions will tend to cancel out. The SNR can also be improved by sampling larger volumes (increasing the field of view and slice thickness with a corresponding loss of spatial resolution) or, within limits, by increasing the strength of the magnetic field used. Surface coils can also be used to improve local signal intensity. The SNR will depend, in part, on the electrical properties of the sample or patient being studied.
The SNR increases in proportion to voxel volume (1/ resolution), the square root of the number of acquisitions ( NEX), and the square root of the number of scans ( phase encodings). SNR decreases with the field of view squared (FOV2) and wider bandwidths. See also Signal Intensity and Spin Density.
Measuring SNR:
Record the mean value of a small ROI placed in the most homogeneous area of tissue with high signal intensity (e.g. white matter in thalamus). Calculate the standard deviation for the largest possible ROI placed outside the object in the image background (avoid ghosting/aliasing or eye movement artifact regions).
The SNR is then:
Mean Signal/Standard Deviation of Background Noise | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Signal to Noise Ratio' (48).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Signal to Noise Ratio' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  | |  |  | Searchterm 'Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Time Resolved Imaging of Contrast Kinetics' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Volumetric Imaging' (4).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Volumetric Imaging' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |