 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Resonance Frequency' found in 1 term [ ] and 13 definitions [ ] and 13 definitions [ ], (+ 13 Boolean[ ], (+ 13 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 16 - 20 (of 27) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3]  [4 5 6] [4 5 6] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Resonance Frequency' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
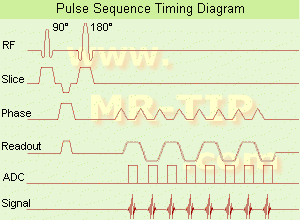
(EPI) Echo planar imaging is one of the early magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like diffusion, perfusion, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other sequences acquire one k-space line at each phase encoding step. When the echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all k-space lines are measured in one repetition time) of a gradient echo or spin echo sequence (see single shot technique) with an acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
The pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an echo planar imaging sequence from spin echo type with eight echo train pulses. (See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the MRI scanner like much larger gradient amplitudes. The scan time is dependent on the spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied gradient fields and the time the machine needs to ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is water fat shift in the phase encoding direction due to phase accumulations. To minimize water fat shift (WFS) in the phase direction fat suppression and a wide bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the flat top of the gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner hardware, in particular on gradient strengths, gradient switching times, and receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions. | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|

It is important to remember when working around a superconducting magnet that the magnetic field is always on. Under usual working conditions the field is never turned off. Attention must be paid to keep all ferromagnetic items at an adequate distance from the magnet. Ferromagnetic objects which came accidentally under the influence of these strong magnets can injure or kill individuals in or nearby the magnet, or can seriously damage every hardware, the magnet itself, the cooling system, etc..
See MRI resources Accidents.
The doors leading to a magnet room should be closed at all times except when entering or exiting the room. Every person working in or entering the magnet room or adjacent rooms with a magnetic field has to be instructed about the dangers. This should include the patient, intensive-care staff, and maintenance-, service- and cleaning personnel, etc..
The 5 Gauss limit defines the 'safe' level of static magnetic field exposure. The value of the absorbed dose is fixed by the authorities to avoid heating of the patient's tissue and is defined by the specific absorption rate.
Leads or wires that are used in the magnet bore during imaging procedures, should not form large-radius wire loops. Leg-to-leg and leg-to-arm skin contact should be prevented in order to avoid the risk of burning due to the generation of high current loops if the legs or arms are allowed to touch. The patient's skin should not be in contact with the inner bore of the magnet.
The outflow from cryogens like liquid helium is improbable during normal operation and not a real danger for patients.
The safety of MRI contrast agents is tested in drug trials and they have a high compatibility with very few side effects. The variations of the side effects and possible contraindications are similar to X-ray contrast medium, but very rare. In general, an adverse reaction increases with the quantity of the MRI contrast medium and also with the osmolarity of the compound.
See also 5 Gauss Fringe Field, 5 Gauss Line, Cardiac Risks, Cardiac Stent, dB/dt, Legal Requirements, Low Field MRI, Magnetohydrodynamic Effect, MR Compatibility, MR Guided Interventions, Claustrophobia, MRI Risks and Shielding. | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Safety' (42).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Safety' (13).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Adiabatic Fast Passage' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Resonance Frequency' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(CSI) Chemical shift imaging is an extension of MR spectroscopy, allowing metabolite information to be measured in an extended region and to add the chemical analysis of body tissues to the potential clinical utility of Magnetic Resonance. The spatial location is phase encoded and a spectrum is recorded at each phase encoding step to allow the spectra acquisition in a number of volumes covering the whole sample. CSI provides mapping of chemical shifts, analog to individual spectral lines or groups of lines.
Spatial resolution can be in one, two or three dimensions, but with long acquisition times od full 3D CSI. Commonly a slice-selected 2D acquisition is used. The chemical composition of each voxel is represented by spectra, or as an image in which the signal intensity depends on the concentration of an individual metabolite. Alternatively frequency-selective pulses excite only a single spectral component.
There are several methods of performing chemical shift imaging, e.g. the inversion recovery method, chemical shift selective imaging sequence, chemical shift insensitive slice selective RF pulse, the saturation method, spatial and chemical shift encoded excitation and quantitative chemical shift imaging.
See also Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Chemical Shift Imaging' (6).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
( CW) A technique for studying NMR by continuously applying RF radiation to the sample and slowly sweeping either the RF frequency or the magnetic field through the resonance values; now largely superceded by pulse MR technique. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Continuous Wave NMR' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |