 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Room Shielding' found in 1 term [ ] and 4 definitions [ ] and 4 definitions [ ], (+ 7 Boolean[ ], (+ 7 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 12) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Room Shielding' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
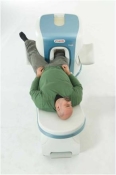
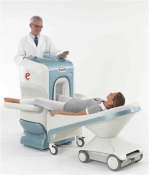
O-scan is manufactured and distributed by Esaote SpA
O-scan is a compact, dedicated extremity MRI system designed for easy installation and high throughput. The complete system fits in a 9' x 10' room, doesn't need for RF or magnetic shielding and it plugs in the wall. The 0.31T permanent magnet along with dual phased array RF coils, and advanced imaging protocols provide outstanding image quality and fast 25 minute complete examinations.
Esaote North America is the exclusive distributor of the O-scan system in the USA.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Dedicated Extremity
PULSE SEQUENCES
SE, HSE, HFE, GE, 2dGE, ME, IR, STIR, Stir T2, GESTIR, TSE, TME, FSE STIR, FSE ( T1, T2), X-Bone, Turbo 3DT1, 3D SHARC, 3D SST1, 3D SST2 2D: 2mm - 10 mm, 3D: 0.6 - 10 mm POWER REQUIREMENTS 100/110/200/220/230/240 | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
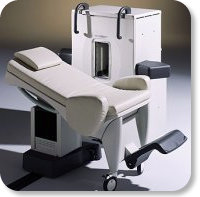
Developed by GE Lunar; the ARTOSCAN™-M is designed specifically for in-office musculoskeletal imaging. ARTOSCAN-M's compact, modular design allows placing within a clinical environment, bringing MRI to the patient. Patients remain outside the magnet at all times during the examinations, enabling constant patient-technologist contact. ARTOSCAN-M requires no special RF room, magnetic shielding, special power supply or air conditioning.
The C-SCAN™ (also known as Artoscan C) is developed from the ARTOSCAN™ - M, with a new computer platform.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Dedicated extremity
SE, GE, IR, STIR, FSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE
SLICE THICKNESS
2D: 2 mm - 10 mm;
3D: 0.6 mm - 10 mm
4,096 gray lvls, 256 lvls in 3D
POWER REQUIREMENTS
100/110/200/220/230/240V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'ARTOSCAN™ - M' (3).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|

It is important to remember when working around a superconducting magnet that the magnetic field is always on. Under usual working conditions the field is never turned off. Attention must be paid to keep all ferromagnetic items at an adequate distance from the magnet. Ferromagnetic objects which came accidentally under the influence of these strong magnets can injure or kill individuals in or nearby the magnet, or can seriously damage every hardware, the magnet itself, the cooling system, etc..
See MRI resources Accidents.
The doors leading to a magnet room should be closed at all times except when entering or exiting the room. Every person working in or entering the magnet room or adjacent rooms with a magnetic field has to be instructed about the dangers. This should include the patient, intensive-care staff, and maintenance-, service- and cleaning personnel, etc..
The 5 Gauss limit defines the 'safe' level of static magnetic field exposure. The value of the absorbed dose is fixed by the authorities to avoid heating of the patient's tissue and is defined by the specific absorption rate.
Leads or wires that are used in the magnet bore during imaging procedures, should not form large-radius wire loops. Leg-to-leg and leg-to-arm skin contact should be prevented in order to avoid the risk of burning due to the generation of high current loops if the legs or arms are allowed to touch. The patient's skin should not be in contact with the inner bore of the magnet.
The outflow from cryogens like liquid helium is improbable during normal operation and not a real danger for patients.
The safety of MRI contrast agents is tested in drug trials and they have a high compatibility with very few side effects. The variations of the side effects and possible contraindications are similar to X-ray contrast medium, but very rare. In general, an adverse reaction increases with the quantity of the MRI contrast medium and also with the osmolarity of the compound.
See also 5 Gauss Fringe Field, 5 Gauss Line, Cardiac Risks, Cardiac Stent, dB/dt, Legal Requirements, Low Field MRI, Magnetohydrodynamic Effect, MR Compatibility, MR Guided Interventions, Claustrophobia, MRI Risks and Shielding. | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI Safety' (42).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI Safety' (13).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Room Shielding' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
In electromagnetism, the Faraday cage or shield is an application of Gauss's law, one of Maxwell's equations. Gauss's law describes the distribution of electrical charge on a conducting form, such as a sphere, a plane, a torus, etc. Intuitively, since like charges repel each other, charge will "migrate" to the surface of the conducting form, as described below. The application is named after physicist Michael Faraday, who built the first Faraday cage in 1836, to demonstrate his finding. A Faraday shield is used generally for any kind of electrostatic shielding.
In MRI, one use of the Faraday shield is the shielding of the scanning room, to block incoming radio frequency (RF) signals which would contaminate the send and received signals of the MRI scanner, and it suppresses RF signals, which would else pollute the environment around. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Faraday Shield' (5).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Magnetic Shielding' (11).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |