 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Shielding' found in 8 terms [ ] and 18 definitions [ ] and 18 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 11 - 15 (of 26) nextResult Pages :  [1 2] [1 2]  [3 4 5 6] [3 4 5 6] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Shielding' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
In electromagnetism, the Faraday cage or shield is an application of Gauss's law, one of Maxwell's equations. Gauss's law describes the distribution of electrical charge on a conducting form, such as a sphere, a plane, a torus, etc. Intuitively, since like charges repel each other, charge will "migrate" to the surface of the conducting form, as described below. The application is named after physicist Michael Faraday, who built the first Faraday cage in 1836, to demonstrate his finding. A Faraday shield is used generally for any kind of electrostatic shielding.
In MRI, one use of the Faraday shield is the shielding of the scanning room, to block incoming radio frequency (RF) signals which would contaminate the send and received signals of the MRI scanner, and it suppresses RF signals, which would else pollute the environment around. | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Shielding' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Quick Overview Please note that there are different common names for this artifact.
DESCRIPTION
Static on the image
REASON
Electromagnetic emissions
HELP
Shielding, eliminate the factor of disturbance
RF noise, which often appears as static on the image, can be caused by a medical device located anywhere in the MR procedure room.
RF noise is a result of excessive electromagnetic emissions from the device that interference with the proper operation of the MR scanner.
The interference is attenuated and aliased in the frequency direction.

Image Guidance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Radio Frequency Noise Artifact' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
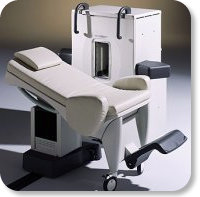
Developed by GE Lunar; the ARTOSCAN™-M is designed specifically for in-office musculoskeletal imaging. ARTOSCAN-M's compact, modular design allows placing within a clinical environment, bringing MRI to the patient. Patients remain outside the magnet at all times during the examinations, enabling constant patient-technologist contact. ARTOSCAN-M requires no special RF room, magnetic shielding, special power supply or air conditioning.
The C-SCAN™ (also known as Artoscan C) is developed from the ARTOSCAN™ - M, with a new computer platform.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Dedicated extremity
SE, GE, IR, STIR, FSE, 3D CE, GE-STIR, 3D GE, ME, TME, HSE
SLICE THICKNESS
2D: 2 mm - 10 mm;
3D: 0.6 mm - 10 mm
4,096 gray lvls, 256 lvls in 3D
POWER REQUIREMENTS
100/110/200/220/230/240V
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'ARTOSCAN™ - M' (3).
| | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Shielding' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Actively Shielded Magnet' (2).
| | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Shielding' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Boil off Rate' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |