 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'Slice Gap' found in 1 term [ ] and 3 definitions [ ] and 3 definitions [ ], (+ 7 Boolean[ ], (+ 7 Boolean[ ] results ] results
| previous 6 - 10 (of 11) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'Slice Gap' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
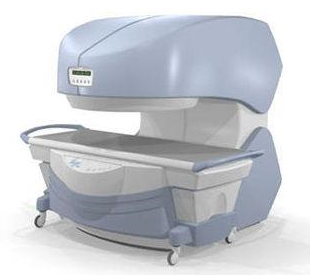
From
Millennium Technology Inc.
This open C-shaped MRI system eases patient comfort and technologist maneuverability. This low cost scanner is build for a wide range of applications. The Virgo™ patient table is detachable and moves on easy rolling castors. Able to accommodate patient weights up to 160 kg, the tabletop has a range of motion of 30 cm in the lateral direction and 90cm in the longitudinal direction. Images generated with this scanner can only be viewed (without data loss) on Millennium's proprietary viewing software.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head, Body, Neck, Knee, Shoulder,
Spine, Wrist, Breast, Extremity, Lumbar Spine, TMJ
IMAGING MODES Localizer, single slice, multi slice, volume, fast, POMP, multi slab, cine, slice and frequency zip, extended dynamic range, tailored RF | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|

From Siemens Medical Systems;
A new, powerful, compact player in MRI. For both, patients and health care professionals, the mid-field has realized a giant step to cost efficient quality care. Obese patients and people with claustrophobia appreciate the comfortable side loading. The smallest pole diameter - 137 cm (54 inches) allows for optimal patient comfort.
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
SE, FLASH, FISP, IR, FIR, STIR, TrueIR/FISP, FSE, MT, SS-FSE, MT-SE, MTC, MSE, EPI, PSIF
IMAGING MODES
Single, multi slice, volume study, multi angle, multi oblique
512 x 512 full screen display
41 cm vertical gap distance
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MAGNETOM C™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(MR mammography) Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast is particularly useful in evaluation of newly diagnosed breast cancer, in women whose breast tissue is mammographically very dense and for screening in women with a high lifetime risk of breast cancer because of their family history or genetic disposition.
Breast MRI can be performed on all standard whole body magnets at a field strength of 0.5 T - 1.5 Tesla. Powerful gradient strengths over 15 mT/m will help to improve the balance between spatial resolution, scanning speed, and volume coverage. The use of a dedicated bilateral breast coil is obligatory.
Malignant lesions release angiogenic factors that increase local vessel density and vessel permeability. Breast cancer is detectable due to the strong enhancement in dynamic breast imaging that peaks early (about 1-2 min.) after contrast medium injection. If breast cancer is suspected, a breast biopsy may be necessary to secure the diagnosis. See also Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI, Biopsy and MR Guided Interventions.
Requirements in breast MRI procedures:
•
Both breasts must be measured without gaps.
•
For the best possible detection of enhancement fat signal should be eliminated either by image subtraction or by
spectrally selective fat saturation.
•
Thin slices are necessary to assure absence of partial
volume effects.
•
Imaging should be performed with a spatial
resolution in plane less than 1 mm.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Breast Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com.
See also the related poll result: ' MRI will have replaced 50% of x-ray exams by' | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Breast MRI' (13).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Breast MRI' (41).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Technology advances in breast cancer screenings lead to early diagnosis
Friday, 6 October 2023 by ksltv.com |  |  |
Are synthetic contrast-enhanced breast MRI images as good as the real thing?
Friday, 18 November 2022 by healthimaging.com |  |  |
Abbreviated breast MRI protocols not as cost-effective as promised, new study shows
Wednesday, 20 July 2022 by healthimaging.com |  |  |
Deep learning poised to improve breast cancer imaging
Thursday, 24 February 2022 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Pre-Operative Breast MRI Can Help Identify Patients Likely to Experience Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Risks
Wednesday, 7 April 2021 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Breast cancer screening recalls: simple MRI measurement could avoid 30% of biopsies
Monday, 1 March 2021 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
A Comparison of Methods for High-Spatial-Resolution Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Breast MRI
Tuesday, 25 August 2020 by pubs.rsna.org |  |  |
Pre-Operative Breast MRI Diagnoses More Cancers in Women with DCIS
Thursday, 9 July 2020 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Breast MRI and tumour biology predict axillary lymph node response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer
Thursday, 26 December 2019 by cancerimagingjournal.biomedcentral.com |  |  |
Breast MRI Coding Gets an Overhaul in 2019
Wednesday, 9 January 2019 by www.aapc.com |  |  |
How accurate are volumetric software programs when compared to breast MRI?
Thursday, 27 July 2017 by www.radiologybusiness.com |  |  |
Additional Breast Cancer Tumors Found on MRI After Mammography May Be Larger, More Aggressive
Wednesday, 9 December 2015 by www.oncologynurseadvisor.com |  |  |
Preoperative MRI May Overdiagnose Contralateral Breast Cancer
Wednesday, 2 December 2015 by www.cancertherapyadvisor.com |  |  |
BI-RADS and breast MRI useful in predicting malignancy
Wednesday, 30 May 2012 by www.oncologynurseadvisor.com |
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Slice Gap' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
A technique, which produces a 3 dimensional image of an object. The advantage of this approach is that the signal, acquired from the entire volume has an increased SNR. ' Slices' are defined by a second phase encoded axis, which divides the volume into 'partitions'.
There is no gap between the slices in 3D volume imaging, therefore thin slices are possible. The Gz phase encoding gradient is set for several slices in one. But 3D takes more time with thin slices because of this phase encoding gradient. With conventional thin slice imaging, the SNR is poor, with 3D volume imaging this is not the case because the slab (volume) is responsible for SNR. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for '3 Dimensional Imaging' (5).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for '3 Dimensional Imaging' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Exited measurement volume for 3D imaging. Slices are defined by a second phase encoded axis, which divides the volume into partitions without a gap. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Slab' (28).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |