 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Spatial Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Low-contrast resolution:
The ability to image objects with similar subjects contrast; contrast detectability.
High-contrast resolution:
The ability to image small objects having high subject contrast and spatial resolution. | |  | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Resolution' (4).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spatial Resolution' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
The Dixon technique is a MRI method used for fat suppression and/or fat quantification. The difference in magnetic resonance frequencies between fat and water-bound protons allows the separation of water and fat images based on the chemical shift effect.
This imaging technique is named after Dixon, who published in 1984 the basic idea to use phase differences to calculate water and fat components in postprocessing. Dixon's method relies on acquiring an image when fat and water are 'in phase', and another in 'opposed phase' ( out of phase). These images are then added together to get water-only images, and subtracted to get fat-only images. Therefore, this sequence type can deliver up to 4 contrasts in one measurement: in phase, opposed phase, water and fat images. An additional benefit of Dixon imaging is that source images and fat images are also available to the diagnosing physician.
The original two point Dixon sequence (number of points means the number of images acquired at different TE) had limited possibilities to optimize the echo time, spatial resolution, slice thickness, and scan time; but Dixon based fat suppression can be very effective in areas of high magnetic susceptibility, where other techniques fail. This insensitivity to magnetic field inhomogeneity and the possibility of direct image-based water and fat quantification have currently generated high research interests and improvements to the basic method (three point Dixon).
The combination of Dixon with gradient echo sequences allows for example liver imaging with 4 image types in one breath hold. With Dixon TSE/FSE an excellent fat suppression with high resolution can be achieved, particularly useful in imaging of the extremities.
For low bandwidth imaging, chemical shift correction of fat images can be made before recombination with water images to produce images free of chemical shift displacement artifacts. The need to acquire more echoes lengthens the minimum scan time, but the lack of fat saturation pulses extends the maximum slice coverage resulting in comparable scan time. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Dixon' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
SE, IR, FSE, FIR, GE, SG, BASG, PBSG, PCIR, DWI, Radial, Angiography: TOF, FLUTE (Fluoro-triggered bolus MRA), Time-resolved MRA
IMAGING MODES
Single, multislice, volume study
Level Range: -2,000 to +4,000
POWER REQUIREMENTS
208/220/240 V, single phase
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Echelon™ 1.5T' (2).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Echelon™ 1.5T' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spatial Resolution' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
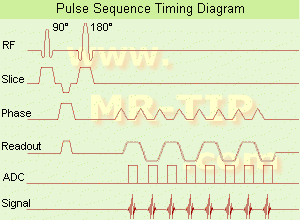
(EPI) Echo planar imaging is one of the early magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like diffusion, perfusion, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other sequences acquire one k-space line at each phase encoding step. When the echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all k-space lines are measured in one repetition time) of a gradient echo or spin echo sequence (see single shot technique) with an acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
The pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an echo planar imaging sequence from spin echo type with eight echo train pulses. (See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the MRI scanner like much larger gradient amplitudes. The scan time is dependent on the spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied gradient fields and the time the machine needs to ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is water fat shift in the phase encoding direction due to phase accumulations. To minimize water fat shift (WFS) in the phase direction fat suppression and a wide bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the flat top of the gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner hardware, in particular on gradient strengths, gradient switching times, and receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Echo Planar Imaging' (19).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Echo Planar Imaging' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Spatial Resolution' was also found in the following service: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Cylindrical Wide Short Bore
Opt. (WIP) Single and Multi Voxel
SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, Hybrid EPI, Multi Shot EPI; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC
IMAGING MODES
Single, multislice, volume study
TE
8 msec min. SE; 1.2 msec min. FE
less than 0.015 (256x256)
1.0 min. 2-DFT: 0.2 min. 3-DFT
32-1024, phase;; 64-1024, freq.
65.5 cm, patient aperture
4050 kg (bare magnet incl. L-He)
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE
Closed-loop water-cooled
Liquid helium: approx. less than 0.05 L/hr
Passive, active, auto-active
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Excelart AG™ with Pianissimo' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |