 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'T1 Relaxation' found in 1 term [ ] and 23 definitions [ ] and 23 definitions [ ] ]
| 1 - 5 (of 24) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |  | |  | Searchterm 'T1 Relaxation' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'T1 Relaxation':    | | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Contrast agents are chemical substances introduced to the anatomical or functional region being imaged, to increase the differences between different tissues or between normal and abnormal tissue, by altering the relaxation times. MRI contrast agents are classified by the different changes in relaxation times after their injection.
•
Negative contrast agents (appearing predominantly dark on MRI) are small particulate aggregates often termed superparamagnetic iron oxide ( SPIO). These agents produce predominantly spin spin relaxation effects (local field inhomogeneities), which results in shorter T1 and T2 relaxation times.
SPIO's and ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides ( USPIO) usually consist of a crystalline iron oxide core containing thousands of iron atoms and a shell of polymer, dextran, polyethyleneglycol, and produce very high T2 relaxivities. USPIOs smaller than 300 nm cause a substantial T1 relaxation. T2 weighted effects are predominant.
•
A special group of negative contrast agents (appearing dark on MRI) are perfluorocarbons ( perfluorochemicals), because their presence excludes the hydrogen atoms responsible for the signal in MR imaging.
The design objectives for the next generation of MR contrast agents will likely focus on prolonging intravascular retention, improving tissue targeting, and accessing new contrast mechanisms. Macromolecular paramagnetic contrast agents are being tested worldwide. Preclinical data shows that these agents demonstrate great promise for improving the quality of MR angiography, and in quantificating capillary permeability and myocardial perfusion.
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide ( USPIO) particles have been evaluated in multicenter clinical trials for lymph node MR imaging and MR angiography, with the clinical impact under discussion. In addition, a wide variety of vector and carrier molecules, including antibodies, peptides, proteins, polysaccharides, liposomes, and cells have been developed to deliver magnetic labels to specific sites. Technical advances in MR imaging will further increase the efficacy and necessity of tissue-specific MRI contrast agents.
See also Adverse Reaction and Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis.
See also the related poll result: ' The development of contrast agents in MRI is' | | | | | | | | | | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Contrast Agents' (122).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Contrast Agents' (25).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Brain imaging method may aid mild traumatic brain injury diagnosis
Tuesday, 16 January 2024 by parkinsonsnewstoday.com |  |  |
A Targeted Multi-Crystalline Manganese Oxide as a Tumor-Selective Nano-Sized MRI Contrast Agent for Early and Accurate Diagnosis of Tumors
Thursday, 18 January 2024 by www.dovepress.com |  |  |
FDA Approves Gadopiclenol for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.pharmacytimes.com |  |  |
How to stop using gadolinium chelates for magnetic resonance imaging: clinical-translational experiences with ferumoxytol
Saturday, 5 February 2022 by www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
Estimation of Contrast Agent Concentration in DCE-MRI Using 2 Flip Angles
Tuesday, 11 January 2022 by pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |  |  |
Manganese enhanced MRI provides more accurate details of heart function after a heart attack
Tuesday, 11 May 2021 by www.news-medical.net |  |  |
Gadopiclenol: positive results for Phase III clinical trials
Monday, 29 March 2021 by www.pharmiweb.co |  |  |
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents Hypersensitivity: A Case Series
Friday, 4 December 2020 by www.dovepress.com |  |  |
Polysaccharide-Core Contrast Agent as Gadolinium Alternative for Vascular MR
Monday, 8 March 2021 by www.diagnosticimaging.com |  |  |
Water-based non-toxic MRI contrast agents
Monday, 11 May 2020 by chemistrycommunity.nature.com |  |  |
New method to detect early-stage cancer identified by Georgia State, Emory research team
Friday, 7 February 2020 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Researchers Brighten Path for Creating New Type of MRI Contrast Agent
Friday, 7 February 2020 by www.newswise.com |  |  |
Manganese-based MRI contrast agent may be safer alternative to gadolinium-based agents
Wednesday, 15 November 2017 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Sodium MRI May Show Biomarker for Migraine
Friday, 1 December 2017 by psychcentral.com |  |  |
A natural boost for MRI scans
Monday, 21 October 2013 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
For MRI, time is of the essence A new generation of contrast agents could make for faster and more accurate imaging
Tuesday, 28 June 2011 by scienceline.org |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(FAIR) In this sequence 2 inversion recovery images are acquired, one with a nonselective and the other with a slice selective inversion pulse. The z-magnetization in the first sequence is independent of flow. Inflowing spins give z-magnetization from second pulse.
A major signal loss in FAIR is the T1 relaxation of tagged blood in transit to the imaging slice. Sharper edges of the inversion pulse give narrow spacing between the inversion edge and the 1st slice because reduced transit time gives lower T1 relaxation induced signal loss.
The difference of the images in a consequence contains information proportional to flow (blood partition coefficient). Standard adiabatic inversion RF pulse does not have good slice-profile, because of power/SAR limitation. A c-shaped frequency offset corrected inversion (FOCI) RF pulse can help to increase the signal.
Perfusion imaging, e.g. myocardial, using tissue water as endogenous contrast is suggested. | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'T1 Relaxation' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
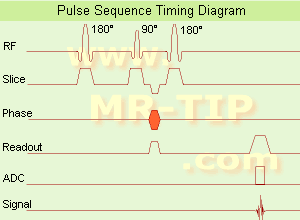
(IR) The inversion recovery pulse sequence produces signals, which represent the longitudinal magnetization existing after the application of a 180° radio frequency pulse that rotates the magnetization Mz into the negative plane. After an inversion time (TI - time between the starting 180° pulse and the following 90° pulse), a further 90° RF pulse tilts some or all of the z-magnetization into the xy-plane, where the signal is usually rephased with a 180° pulse as in the spin echo sequence. During the initial time period, various tissues relax with their intrinsic T1 relaxation time.
In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the basic inversion recovery sequence is illustrated. The 180° inversion pulse is attached prior to the 90° excitation pulse of a spin echo acquisition.
See also the Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram. There you will find a description of the components.
The inversion recovery sequence has the advantage, that it can provide very strong contrast between tissues having different T1 relaxation times or to suppress tissues like fluid or fat.
But the disadvantage is, that the additional inversion radio frequency RF pulse makes this sequence less time efficient than the other pulse sequences.
Contrast values:
PD weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 1800 ms
T1 weighted: TE: 10-20 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
T2 weighted: TE: 70 ms, TR: 2000 ms, TI: 400-800 ms
See also Inversion Recovery, Short T1 Inversion Recovery, Fluid Attenuation Inversion Recovery, and Acronyms for 'Inversion Recovery Sequence' from different manufacturers. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Inversion Recovery Sequence' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
The T1 relaxation time (also called spin lattice or longitudinal relaxation time), is a biological parameter that is used in MRIs to distinguish between tissue types. This tissue-specific time constant for protons, is a measure of the time taken to realign with the external magnetic field. The T1 constant will indicate how quickly the spinning nuclei will emit their absorbed RF into the surrounding tissue.
As the high-energy nuclei relax and realign, they emit energy which is recorded to provide information about their environment. The realignment with the magnetic field is termed longitudinal relaxation and the time in milliseconds required for a certain percentage of the tissue nuclei to realign is termed 'Time 1' or T1. Starting from zero magnetization in the z direction, the z magnetization will grow after excitation from zero to a value of about 63% of its final value in a time of T1. This is the basic of T1 weighted images.
The T1 time is a contrast determining tissue parameter. Due to the slow molecular motion of fat nuclei, longitudinal relaxation occurs rather rapidly and longitudinal magnetization is regained quickly. The net magnetic vector realigns with B0 leading to a short T1 time for fat.
Water is not as efficient as fat in T1 recovery due to the high mobility of the water molecules. Water nuclei do not give up their energy to the lattice (surrounding tissue) as quickly as fat, and therefore take longer to regain longitudinal magnetization, resulting in a long T1 time.
See also T1 Weighted Image, T1 Relaxation, T2 Weighted Image, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'T1 Time' (15).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 24) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5] [2 3 4 5] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |