 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'perfusion' found in 2 terms [ ] and 33 definitions [ ] and 33 definitions [ ] ]
| previous 16 - 20 (of 35) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3 4 5 6 7] [2 3 4 5 6 7] |  | |  | Searchterm 'perfusion' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
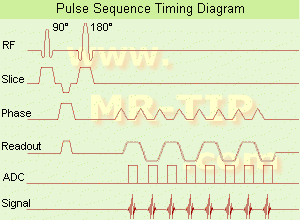
(EPI) Echo planar imaging is one of the early magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like diffusion, perfusion, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other sequences acquire one k-space line at each phase encoding step. When the echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all k-space lines are measured in one repetition time) of a gradient echo or spin echo sequence (see single shot technique) with an acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
The pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an echo planar imaging sequence from spin echo type with eight echo train pulses. (See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the MRI scanner like much larger gradient amplitudes. The scan time is dependent on the spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied gradient fields and the time the machine needs to ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is water fat shift in the phase encoding direction due to phase accumulations. To minimize water fat shift (WFS) in the phase direction fat suppression and a wide bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the flat top of the gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner hardware, in particular on gradient strengths, gradient switching times, and receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions. | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
From ISOL Technology
'Ultra high field MR system, it's right close to you.
FORTE 3.0T is the new standard for the future ultra high field MR system.
If you are pushing the limits of your existing clinical MR scanner, the FORTE will surely take you to the next level of diagnostic imaging.
FORTE is the core leader of the medical technology in the 21st century. Proving effects of fMRI that cannot be measured with MRI less than 2.0T.'
Device Information and Specification
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Whole body
CONFIGURATION
Short bore compact
128 x 128, 256 x 256, 512 x 512, 1024 x 1024
| |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'FORTE 3.0T™' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
Flow phenomena are intrinsic processes in the human body. Organs like the heart, the brain or the kidneys need large amounts of blood and the blood flow varies depending on their degree of activity. Magnetic resonance imaging has a high sensitivity to flow and offers accurate, reproducible, and noninvasive methods for the quantification of flow. MRI flow measurements yield information of blood supply of of various vessels and tissues as well as cerebro spinal fluid movement.
Flow can be measured and visualized with different pulse sequences (e.g. phase contrast sequence, cine sequence, time of flight angiography) or contrast enhanced MRI methods (e.g. perfusion imaging, arterial spin labeling).
The blood volume per time (flow) is measured in: cm3/s or ml/min. The blood flow-velocity decreases gradually dependent on the vessel diameter, from approximately 50 cm per second in arteries with a diameter of around 6 mm like the carotids, to 0.3 cm per second in the small arterioles.
Different flow types in human body:
•
Behaves like stationary tissue, the signal intensity depends on T1, T2 and PD = Stagnant flow
•
Flow with consistent velocities across a vessel = Laminar flow
•
Laminar flow passes through a stricture or stenosis (in the center fast flow, near the walls the flow spirals) = Vortex flow
•
Flow at different velocities that fluctuates = Turbulent flow
See also Flow Effects, Flow Artifact, Flow Quantification, Flow Related Enhancement, Flow Encoding, Flow Void, Cerebro Spinal Fluid Pulsation Artifact, Cardiovascular Imaging and Cardiac MRI. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Flow' (113).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Flow' (7).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'perfusion' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
(FAIR) In this sequence 2 inversion recovery images are acquired, one with a nonselective and the other with a slice selective inversion pulse. The z-magnetization in the first sequence is independent of flow. Inflowing spins give z-magnetization from second pulse.
A major signal loss in FAIR is the T1 relaxation of tagged blood in transit to the imaging slice. Sharper edges of the inversion pulse give narrow spacing between the inversion edge and the 1st slice because reduced transit time gives lower T1 relaxation induced signal loss.
The difference of the images in a consequence contains information proportional to flow (blood partition coefficient). Standard adiabatic inversion RF pulse does not have good slice-profile, because of power/SAR limitation. A c-shaped frequency offset corrected inversion (FOCI) RF pulse can help to increase the signal.
Perfusion imaging, e.g. myocardial, using tissue water as endogenous contrast is suggested. | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
(fMRI) Functional magnetic resonance imaging is a technique used to determine the dynamic brain function, often based on echo planar imaging, but can also be performed by using contrast agents and observing their first pass effects through brain tissue. Functional magnetic resonance imaging allows insights in a dysfunctional brain as well as into the basic workings of the brain.
The in functional brain MRI most frequently used effect to assess brain function is the blood oxygenation level dependent contrast ( BOLD) effect, in which differential changes in brain perfusion and their resultant effect on the regional distribution of oxy- to deoxyhaemoglobin are observable because of the different 'intrinsic contrast media' effects of the two haemoglobin forms. Increased brain activity causes an increased demand for oxygen, and the vascular system actually overcompensates for this, increasing the amount of oxygenated haemoglobin. Because deoxygenated haemoglobin attenuates the MR signal, the vascular response leads to a signal increase that is related to the neural activity.
Functional imaging relates body function or thought to specific locations where the neural activity is taking place. The brain is scanned at low resolution but at a fast rate (typically once every 2-3 seconds). Structural MRI together with fMRI provides an anatomical baseline and best spatial resolution.
Interactions can also be seen from the motor cortex to the cerebellum or basal ganglia in the case of a movement disorder such as ataxia. For example: by a finger movement the briefly increase in the blood circulation of the appropriate part of the brain controlling that movement, can be measured. | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging' (8).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging' (15).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |