 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
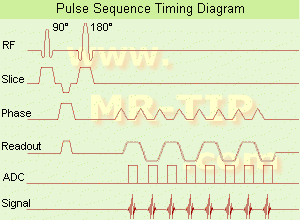
(EPI) Echo planar imaging is one of the early magnetic resonance imaging sequences (also known as Intascan), used in applications like diffusion, perfusion, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Other sequences acquire one k-space line at each phase encoding step. When the echo planar imaging acquisition strategy is used, the complete image is formed from a single data sample (all k-space lines are measured in one repetition time) of a gradient echo or spin echo sequence (see single shot technique) with an acquisition time of about 20 to 100 ms.
The pulse sequence timing diagram illustrates an echo planar imaging sequence from spin echo type with eight echo train pulses. (See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram, for a description of the components.)
In case of a gradient echo based EPI sequence the initial part is very similar to a standard gradient echo sequence. By periodically fast reversing the readout or frequency encoding gradient, a train of echoes is generated.
EPI requires higher performance from the MRI scanner like much larger gradient amplitudes. The scan time is dependent on the spatial resolution required, the strength of the applied gradient fields and the time the machine needs to ramp the gradients.
In EPI, there is water fat shift in the phase encoding direction due to phase accumulations. To minimize water fat shift (WFS) in the phase direction fat suppression and a wide bandwidth (BW) are selected. On a typical EPI sequence, there is virtually no time at all for the flat top of the gradient waveform. The problem is solved by "ramp sampling" through most of the rise and fall time to improve image resolution.
The benefits of the fast imaging time are not without cost. EPI is relatively demanding on the scanner hardware, in particular on gradient strengths, gradient switching times, and receiver bandwidth. In addition, EPI is extremely sensitive to image artifacts and distortions. | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
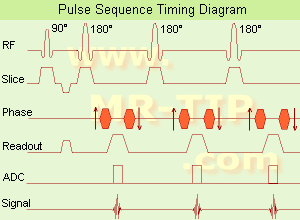
(FSE) In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast spin echo sequence with an echo train length of 3 is illustrated.
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180° rephasing pulses and multiple echoes, changing the phase encoding gradient for each echo.
The echo time TE may vary from echo to echo in the echo train. The echoes in the center of the K-space (in the case of linear k-space acquisition) mainly produce the type of image contrast, whereas the periphery of K-space determines the spatial resolution. For example, in the middle of K-space the late echoes of T2 weighted images are encoded. T1 or PD contrast is produced from the early echoes.
The benefit of this technique is that the scan duration with, e.g. a turbo spin echo turbo factor / echo train length of 9, is one ninth of the time. In T1 weighted and proton density weighted sequences, there is a limit to how large the ETL can be (e.g. a usual ETL for T1 weighted images is between 3 and 7). The use of large echo train lengths with short TE results in blurring and loss of contrast. For this reason, T2 weighted imaging profits most from this technique.
In T2 weighted FSE images, both water and fat are hyperintense. This is because the succession of 180° RF pulses reduces the spin spin interactions in fat and increases its T2 decay time. Fast spin echo (FSE) sequences have replaced conventional T2 weighted spin echo sequences for most clinical applications. Fast spin echo allows reduced acquisition times and enables T2 weighted breath hold imaging, e.g. for applications in the upper abdomen.
In case of the acquisition of 2 echoes this type of a sequence is named double fast spin echo / dual echo sequence, the first echo is usually density and the second echo is T2 weighted image. Fast spin echo images are more T2 weighted, which makes it difficult to obtain true proton density weighted images. For dual echo imaging with density weighting, the TR should be kept between 2000 - 2400 msec with a short ETL (e.g., 4).
Other terms for this technique are:
Turbo Spin Echo
Rapid Imaging Spin Echo,
Rapid Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition Spin Echo,
Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Fast Spin Echo' (31).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
In fast imaging sequences driven equilibrium sensitizes the sequence to variations in T2. This MRI technique turns transverse magnetization Mxy to the longitudinal axis using a pulse rather than waiting for T1 relaxation.
The first two pulses form a spin echo and, at the peak of the echo, a second 90° pulse returns the magnetization to the z-axis in preparation for a fresh sequence.
In the absence of T2 relaxation, then all the magnetization can be returned to the z-axis. Otherwise, T2 signal loss during the sequence will reduce the final z-magnetization.
The advantage of this sequence type is, that both longitudinal and also transverse magnetization are back to equilibrium in a shorter amount of time. Therefore, contrast and signal can be increased while using a shorter TR. This pulse type can be applied to other sequences like FSE, GE or IR.
Sequences with driven equilibrium:
Driven Equilibrium Fast Gradient Recalled acquisition in the steady state - DE FGR,
Driven Equilibrium Fourier Transformation - DEFT,
Driven Equilibrium magnetization preparation - DE prep,
Driven Equilibrium Fast Spin Echo - DE FSE. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Driven Equilibrium' (8).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'sequence' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
General MRI of the abdomen can consist of T1 or T2 weighted spin echo, fast spin echo ( FSE, TSE) or gradient echo sequences with fat suppression and contrast enhanced MRI techniques. The examined organs include liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenals as well as parts of the stomach and intestine (see also gastrointestinal imaging). Respiratory compensation and breath hold imaging is mandatory for a good image quality.
T1 weighted sequences are more sensitive for lesion detection than T2 weighted sequences at 0.5 T, while higher field strengths (greater than 1.0 T), T2 weighted and spoiled gradient echo sequences are used for focal lesion detection.
Gradient echo in phase T1 breath hold can be performed as a dynamic series with the ability to visualize the blood distribution. Phases of contrast enhancement include the capillary or arterial dominant phase for demonstrating hypervascular lesions, in liver imaging the portal venous phase demonstrates the maximum difference between the liver and hypovascular lesions, while the equilibrium phase demonstrates interstitial disbursement for edematous and malignant tissues.
Out of phase gradient echo imaging for the abdomen is a lipid-type tissue sensitive sequence and is useful for the visualization of focal hepatic lesions, fatty liver (see also Dixon), hemochromatosis, adrenal lesions and renal masses.
The standards for abdominal MRI vary according to clinical sites based on sequence availability and MRI equipment.
Specific abdominal imaging coils and liver-specific contrast agents targeted to the healthy liver tissue improve the detection and localization of lesions.
See also Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents, Reticuloendothelial Contrast Agents, and Oral Contrast Agents.
For Ultrasound Imaging (USI) see Abdominal Ultrasound at Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com. | | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Abdominal Imaging' (11).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Abdominal Imaging' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
|  |
Assessment of Female Pelvic Pathologies: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Patients Undergoing Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Pelvic Assessment at the Maternity and Children Hospital, Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia
Saturday, 7 October 2023 by www.cureus.com |  |  |
Higher Visceral, Subcutaneous Fat Levels Predict Brain Volume Loss in Midlife
Wednesday, 4 October 2023 by www.neurologyadvisor.com |  |  |
Deep Learning Helps Provide Accurate Kidney Volume Measurements
Tuesday, 27 September 2022 by www.rsna.org |  |  |
CT, MRI for pediatric pancreatitis interobserver agreement with INSPPIRE
Friday, 11 March 2022 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Clinical trial: Using MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis equals or beats current standard
Thursday, 4 February 2021 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
Computer-aided detection and diagnosis for prostate cancer based on mono and multi-parametric MRI: A review - Abstract
Tuesday, 28 April 2015 by urotoday.com |  |  |
Nottingham scientists exploit MRI technology to assist in the treatment of IBS
Thursday, 9 January 2014 by www.news-medical.net |  |  |
New MR sequence helps radiologists more accurately evaluate abnormalities of the uterus and ovaries
Thursday, 23 April 2009 by www.eurekalert.org |  |  |
MRI identifies 'hidden' fat that puts adolescents at risk for disease
Tuesday, 27 February 2007 by www.eurekalert.org |
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Balanced Fast Field Echo' (3).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |