 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | |
Result : Searchterm 'toshiba' found in 1 term [ ] and 10 definitions [ ] and 10 definitions [ ] ]
| 1 - 5 (of 11) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |  | |  | Searchterm 'toshiba' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
 [This entry is marked for removal.]
Toshiba
[This entry is marked for removal.]
Toshiba Medical Systems started 1914 and was a leading diagnostic imaging manufacturer with departments including research, development, production, service and support of medical imaging equipment and systems. 1976 Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. (TAMS) was founded to coordinate sales and service for previously established business operations in the USA.
In March 2016 Toshiba sold its Toshiba Medical Systems for $6 billion to Japan's Canon. After regulatory approval the company got renamed to Canon Medical Systems.
MRI Scanners:
0.2T to 1.0T:
1.5T:
3.0T:
| |  | | | | • Share the entry 'Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.':    | | |
• View the NEWS results for 'Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.' (10).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
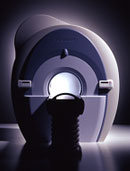
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
With its high-field strength, the Vantage™ delivers the clinical capabilities and image quality expected by cardiologists, while simultaneously offering patients a more comfortable and non-invasive option, said Dane Peshe, director, MRI Business Unit, Toshiba America Medical Systems. Vantage™ supports a full complement of cardiovascular imaging studies, ranging from stroke evaluation to peripheral vascular imaging. Additionally, the ultra short bore design offers patients a greater feeling of openness that reduces claustrophobic sensations, while Toshiba's exclusive, patented Pianissimo™ technology reduces scan noise by as much as 90 percent for a more pleasant experience.'
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body CONFIGURATION Ultra short bore SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, EPI, SuperFASE; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study 32-1024, phase;; 64-1024, freq. POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled Liquid helium: approx. less than 0.05 L/hr Passive, active, auto-active | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Vantage™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | Basics:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
•
In the 1930's, Isidor Isaac Rabi (Columbia University) succeeded in detecting and measuring single states of rotation of atoms and molecules, and in determining the mechanical and magnetic moments of the nuclei.
•
Felix Bloch (Stanford University) and Edward Purcell (Harvard University) developed instruments, which could measure the magnetic resonance in bulk material such as liquids and solids. (Both honored with the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1952.) [The birth of the NMR spectroscopy]
•
In the early 70's, Raymond Damadian (State University of New York) demonstrated with his NMR device, that there are different T1 relaxation times between normal and abnormal tissues of the same type, as well as between different types of normal tissues.
•
In 1973, Paul Lauterbur (State University of New York) described a new imaging technique that he termed Zeugmatography. By utilizing gradients in the magnetic field, this technique was able to produce a two-dimensional image (back-projection). (Through analysis of the characteristics of the emitted radio waves, their origin could be determined.) Peter Mansfield further developed the utilization of gradients in the magnetic field and the mathematically analysis of these signals for a more useful imaging technique. (Paul C Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield were awarded with the 2003 Nobel Prize in Medicine.)
•
1977/78: First images could be presented.
A cross section through a finger by Peter Mansfield and Andrew A. Maudsley.
Peter Mansfield also could present the first image through the abdomen.
•
In 1977, Raymond Damadian completed (after 7 years) the first MR scanner (Indomitable). In 1978, he founded the FONAR Corporation, which manufactured the first commercial MRI scanner in 1980. Fonar went public in 1981.
•
1981: Schering submitted a patent application for Gd-DTPA dimeglumine.
•
1982: The first 'magnetization-transfer' imaging by Robert N. Muller.
•
In 1983, Toshiba obtained approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan for the first commercial MRI system.
•
1986: Jürgen Hennig, A. Nauerth, and Hartmut Friedburg (University of Freiburg) introduced RARE (rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement) imaging. Axel Haase, Jens Frahm, Dieter Matthaei, Wolfgang Haenicke, and Dietmar K. Merboldt (Max-Planck-Institute, Göttingen) developed the FLASH ( fast low angle shot) sequence.
•
1988: Schering's MAGNEVIST gets its first approval by the FDA.
•
In 1991, fMRI was developed independently by the University of Minnesota's Center for Magnetic Resonance Research (CMRR) and Massachusetts General Hospital's (MGH) MR Center.
•
From 1992 to 1997 Fonar was paid for the infringement of it's patents from 'nearly every one of its competitors in the MRI industry including giant multi-nationals as Toshiba, Siemens, Shimadzu, Philips and GE'.
| | | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'MRI History' (6).
| | |
• View the NEWS results for 'MRI History' (1).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'toshiba' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
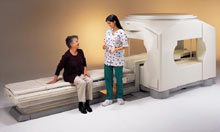
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
the Ultra™ system was developed to help healthcare providers be more competitive by delivering greater patient comfort and a broad range of clinical capabilities, says Anita Bowler, product manager, MRI Business Unit, Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc With its unique, powerful gradient technology, the Ultra™ performs advanced clinical studies and consistently provides high-resolution images that are typically associated with high field MRI systems. At the same time, the Ultra™ offers a truly open feeling that makes patients more relaxed, especially those with claustrophobic tendencies.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole Body Quadrature, solenoid and multi-channel configurations SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, Hybrid EPI, Multi Shot EPI, Single shot EPI diffusion, True SSFP, SuperFASE; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC, Black Blood MRA POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Cryogenless | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|
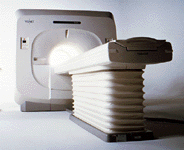
From Toshiba America Medical Systems Inc.;
VISART™ series is a 1.5 Tesla superconducting MRI system that has been designed to meet the expanding role of MRI in today's clinical environment. The system utilizes innovative technologies such as digital RF, high speed actively shielded gradients and optimized RF coils, which support a wide range of MRI developments. The Visart, an early type of Toshiba Medical Systems Inc., can be retrofitted or upgraded to the Excelart configuration.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Quadrature, solenoid and multi-channel configurations SE, FE, IR, FastSE, FastIR, FastFLAIR, Fast STIR, FastFE, FASE, Hybrid EPI, Multi Shot EPI; Angiography: 2D(gate/non-gate)/3D TOF, SORS-STC IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study POWER REQUIREMENTS 380/400/415/440/480 V COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'VISART™' (2).
| | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | News & More:
|
|
| |
|  | |  |  |
|  | |
|  | 1 - 5 (of 11) nextResult Pages :  [1] [1]  [2 3] [2 3] |
| |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |